Child and Forced Labour
The Child and Forced Labour indicator measures legislation regulating the employment of children and linking this employment to their compulsory education.
The indicator also measures whether legislation prohibits forced labour.
9.1 Employment Age
Does the law prohibit employment of children?
International Regulatory Standard
Article 2 of Minimum Age Convention 1973 (No. 138) states that a minimum age for admission to employment or work shall not be less than the age of completion of compulsory schooling and, in any case, shall not be less than 15 years.
However, a ratifying Member whose economy and educational facility are insufficiently developed may, after consultation with the organisations of employers and workers concerned, initially specify a minimum age of 14 years.
Article 32(2) of the Convention on the Rights of the Child can be applied here as well. It states that the States Parties shall take legislative, administrative, social and educational measures to ensure the implementation of a minimum age or minimum age for admission to employment; provide for appropriate regulation of the hours and conditions of employment; Provide for appropriate penalties or other sanctions to ensure the effective enforcement of the present article.
Methodology
Whether the law prohibits the employment of children:
1: The legislation prohibits the employment of children under the age of 15 years (14 years in the case of developing countries).
0: The employment entry age is lower than 15 years (14 years in the case of developing countries).
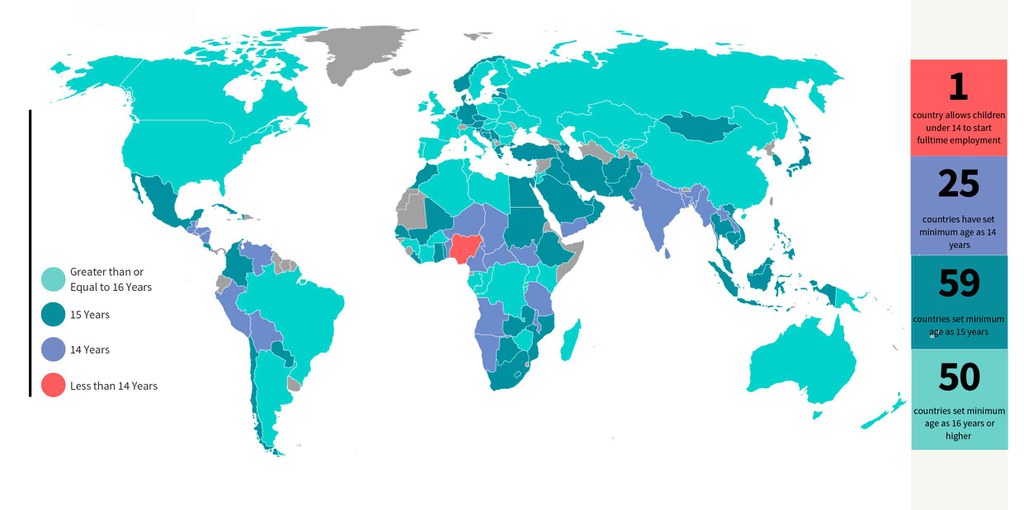
19% of the assessed countries, spread across Africa, Americas and Asia, set the minimum age for employment at 14.
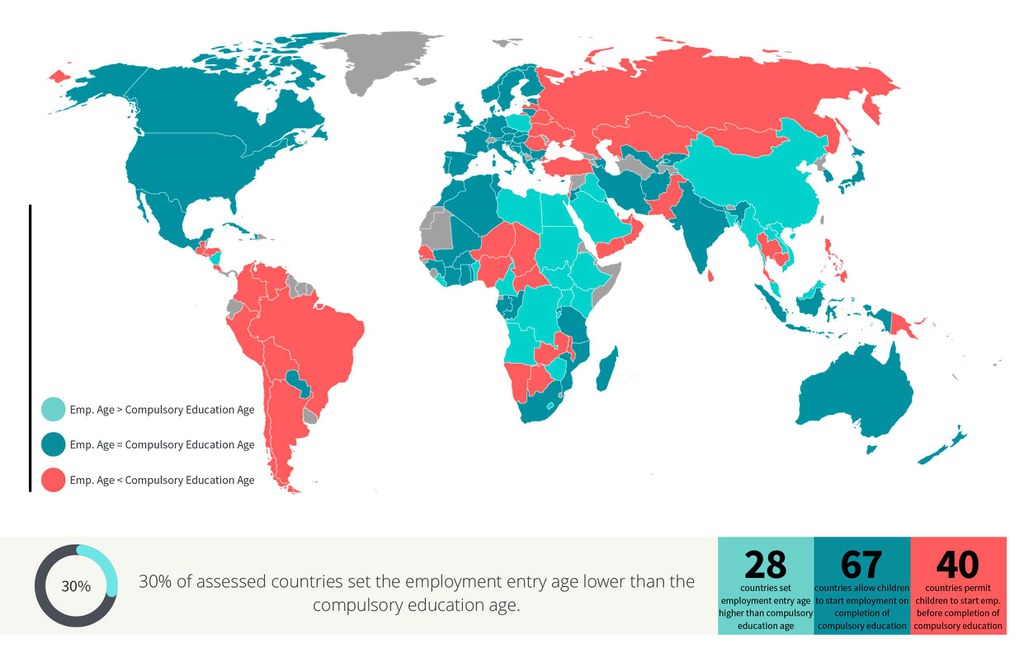
9.2 Compulsory Schooling Age
Does the law set employment entry age equal or higher than the compulsory schooling age?
International Regulatory Standard
Article 2(3) of Minimum Age Convention 1973 (No. 138) specifies that the minimum age for employment shall not be less than the age of completion of compulsory schooling and, in any case, shall not be less than 15 years (14 years for developing countries).
Methodology
Whether employment entry age is similar or higher than the compulsory education age:
1: The legislation sets the employment entry age similar to or higher than the compulsory education age.
0: The employment entry age is lower than the compulsory education age or if the compulsory schooling age is not defined under the law.
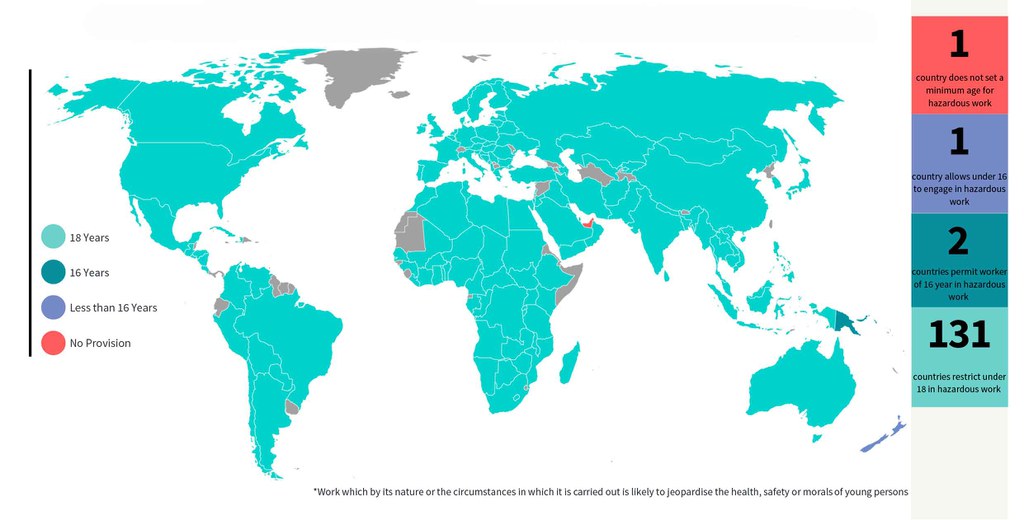
9.3 Age for Hazardous Work
Does the law prohibit the employment of children in hazardous work under the age of 18 years?
International Regulatory Standard
Article 3 of Minimum Age Convention 1973 (No. 138) stipulates that the minimum age for admission to any type of employment or work which, by its nature, or the circumstances in which it is carried out, is likely to jeopardise the health, safety or morals of young persons shall not be less than 18 years. The types of employment or work shall be determined by national laws or regulations or by the competent authority, after consultation with the organisations of employers and workers concerned, where such exist. National laws or regulations or the competent authority may authorise employment or work from the age of 16 years on the condition that the health, safety and morals of the young persons concerned are fully protected and that the young persons have received adequate specific instruction or vocational training in the relevant branch of activity.
Furthermore, Article 32 (1) of the Convention on Rights of Child states that there should be recognition of the right of the child to be protected from economic exploitation and from performing any work that is likely to be hazardous or to interfere with the child’s education, or to be harmful to the child’s health or physical, mental, spiritual, moral or social development.
Methodology
Whether the law prohibits the employment of adolescents in hazardous work:
1: The legislation prohibits the employment of children under the age of 18 years in hazardous work.*
0: The employment entry age for hazardous work is lower than 18 years or is not specified.
97% of the assessed countries set the minimum age for hazardous work at 18, making it a global standard.
9.4 Forced Labour
Does the law prohibit forced labour?
International Regulatory Standard
Article 2 of the Forced Labour Convention, 1930 (No. 29) specifies that forced or compulsory labour means all work or service (with some exceptions) which is exacted from any person under the menace of any penalty and for which the said person has not offered himself voluntarily.
Protocol of 2014 to the Forced Labour Convention, 1930 focuses on taking effective measures to prevent and eliminate the use of forced or compulsory labour, to provide protection to victims and access to appropriate and effective remedies, such as compensation, and sanction the perpetrators of forced or compulsory labour. It also refers to specific action against trafficking in persons for the purposes of forced or compulsory labour.
Article 8 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights states that no one shall be held in slavery or servitude; slavery and the slave trade in all their forms shall be prohibited, and no one shall be required to perform forced or compulsory labour.
Methodology
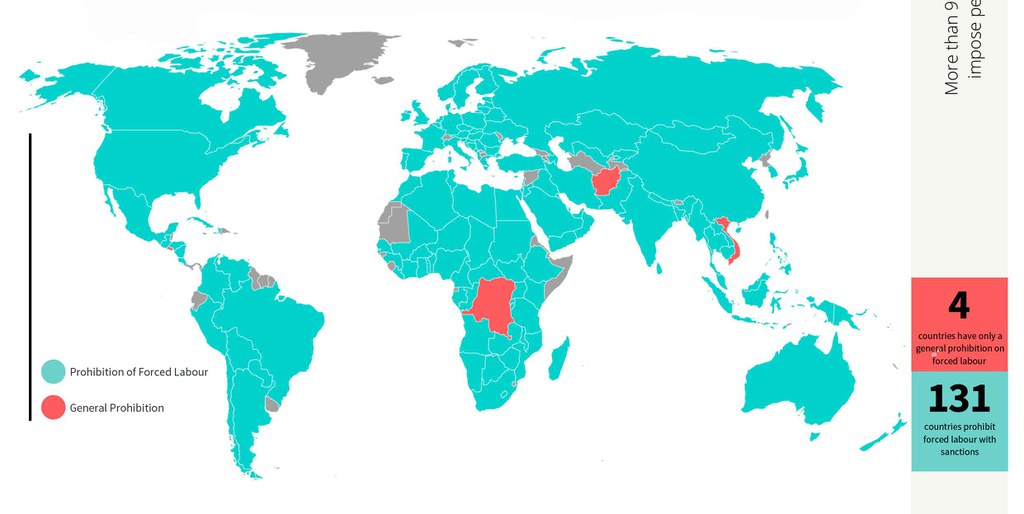
Whether the law prohibits forced labour:
1: The legislation prohibits forced labour except in certain extraordinary circumstances.
0: The law does not prohibit forced labour or has only a general prohibition without any sanctions.
More than 95% of the countries prohibit forced labour and impose penal sanction on those involved in the crime.
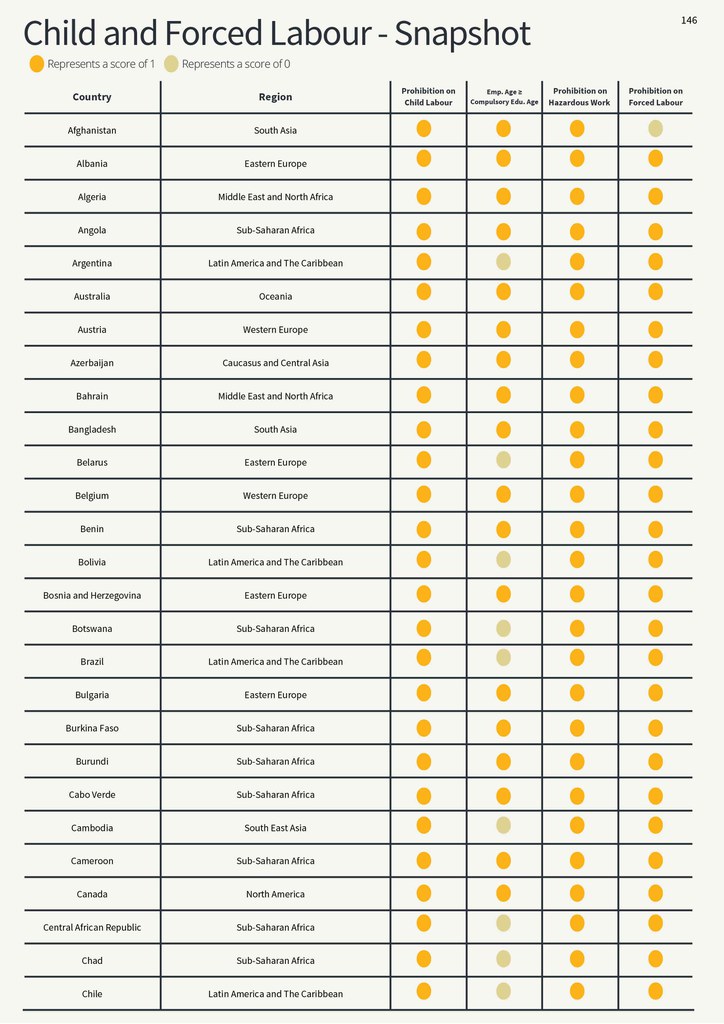
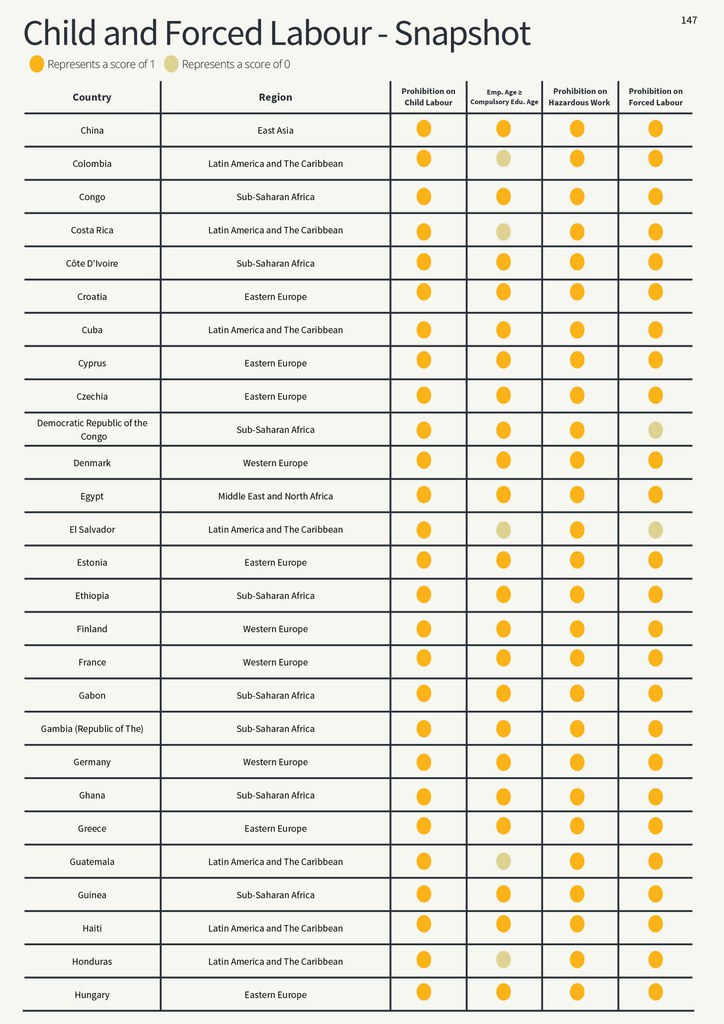
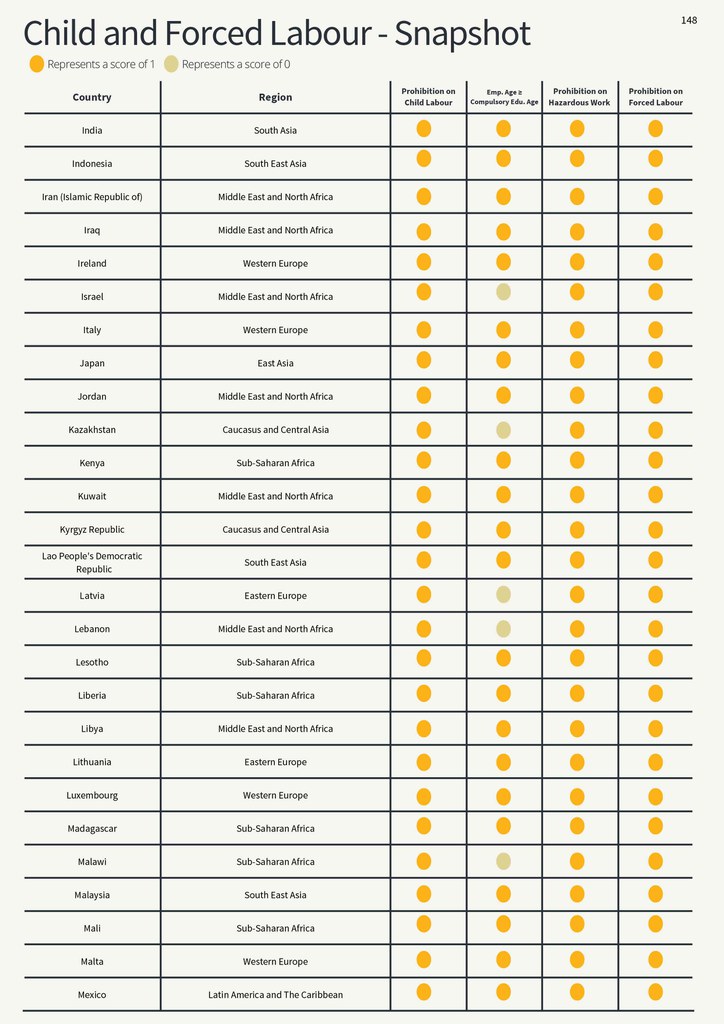
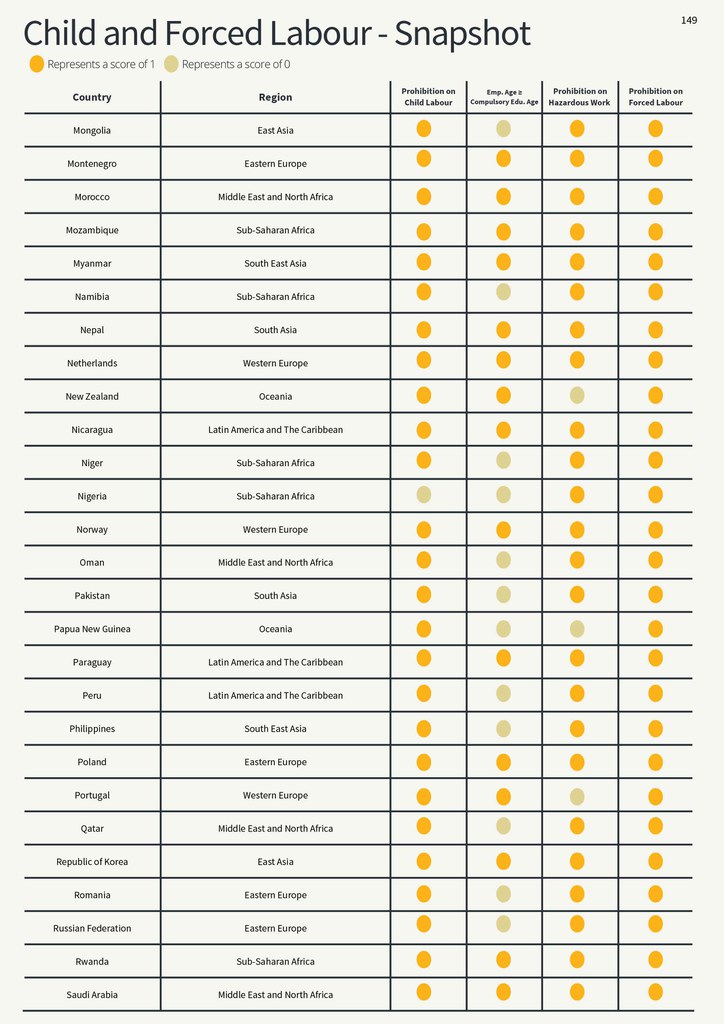
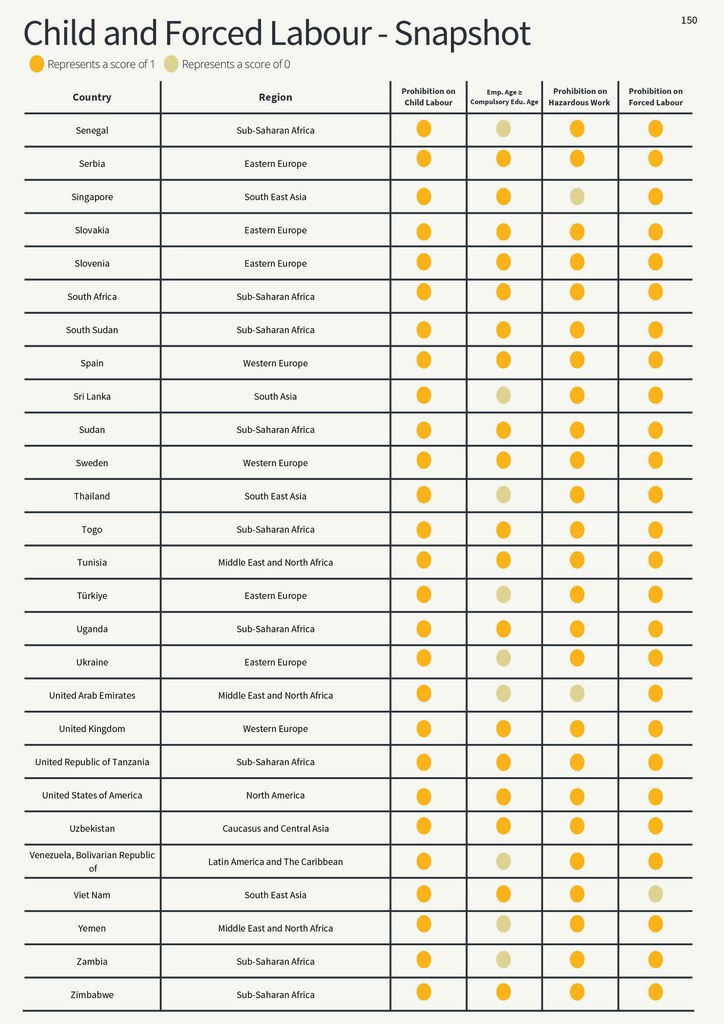
Child and Forced Labour - Snapshot