Adequate social protection is an important aspect of decent work. Protection from the major risks in life through social protection helps keep people out of poverty. It prevents them from being thrown into poverty when unforeseen catastrophes occur, such as an accident, an illness, loss of a job or in old age when work becomes impossible or very difficult.
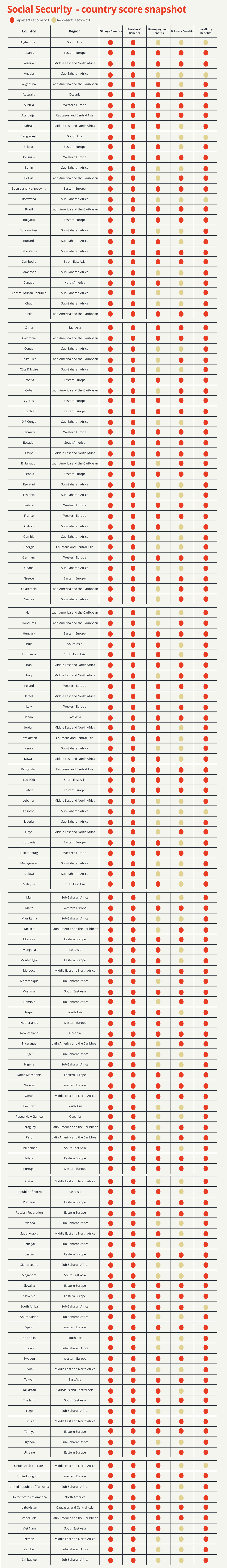
7.1 Old Age Benefits
Does the law provide for an old age benefit?
International Regulatory Standard
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
Article 67 of the ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of old-age benefits at the rate of 40 percent of a worker’s former wage, where the contingency covered shall be survival beyond a prescribed age of not more than 65 years or such higher age as may be fixed by the competent authority with due regard to the working ability of elderly persons in the country concerned.
National laws or regulations may provide that the benefit of a person otherwise entitled to it may be suspended if such person is engaged in any prescribed gainful activity or that the benefit, if contributory, may be reduced where the earnings of the beneficiary exceed a prescribed amount and, if non-contributory, may be reduced where the earnings of the beneficiary or his other means or the two taken together exceed a prescribed amount. The benefit shall be a periodic payment.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law provides for an old-age benefit:
1: Legislation stipulates contributory old-age benefits, or old-age benefits are paid through a non-contributory universal benefits system (both administered by the state) or if there is a provision for non-state-administered old-age benefits*
0: There is no explicit provision for the old-age benefits or if the old-age benefits are only an employer liability.
*Due to nonstandard calculations for old age pension, the value of 40% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler methodology for this component.
**Provident Fund and Individual Mandatory Account
*** There is a minor revision in methodology here. The earlier methodology gave a country a score of 0 if old age benefits were means-tested. Although this condition was in line with Part V of Convention No. 102, this conditionality has now been removed, and scores are adjusted for the following countries:
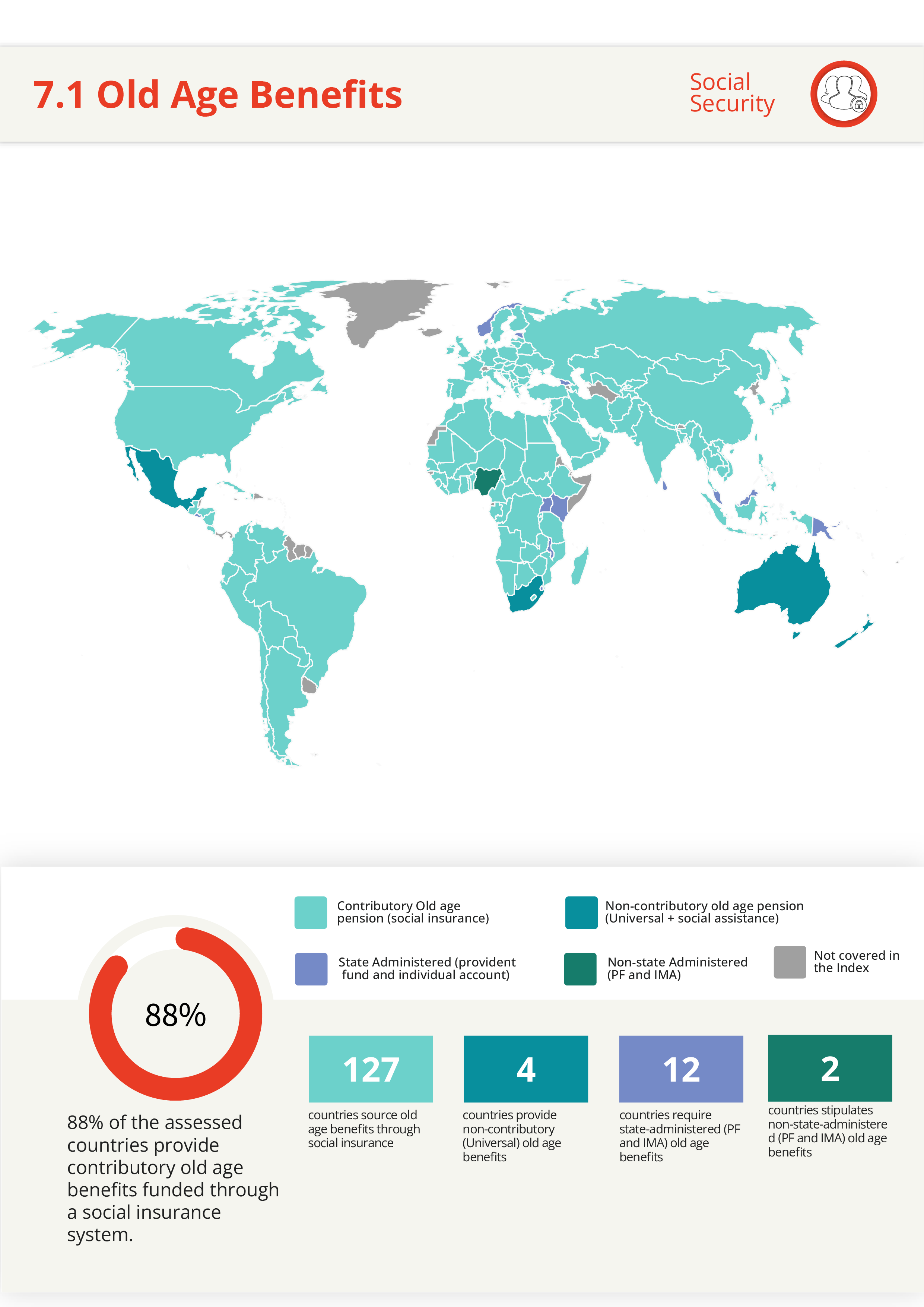
7.2 Survivors' Benefits
Does the law provide for survivors' benefits?
International Regulatory Standard
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
Article 67 of the ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of survivors’ benefits for wives and children of breadwinners at the rate of at least 40 percent of the worker’s wage, where the contingency covered shall include the loss of support suffered by the widow or child as the result of the death of the breadwinner; in the case of a widow, the right to benefit may be made conditional on her being presumed, in accordance with national laws or regulations, to be incapable of self-support.
National laws or regulations may provide that the benefit of a person otherwise entitled to it may be suspended if such person is engaged in any prescribed gainful activity or that the benefit, if contributory, may be reduced where the earnings of the beneficiary exceed a prescribed amount, and, if noncontributory, may be reduced where the earnings of the beneficiary or his other means or the two taken together exceed a prescribed amount. The benefit shall be periodic payment.
Methodology
Whether the legislation provides for survivors' /dependents’ benefits:
1: The legislation provides for contributory social insurance or non-contributory universal benefits for the survivors’ or dependents’ benefits in the event of workers’ or pensioners’ death once they are eligible for old-age or disability benefits (both administered by the state) or if there is a provision for non- state-administered survivors’ benefits.*
0: There is no explicit provision for survivors’ benefits or if the survivors’ benefits are only an employer’s liability.
*Due to nonstandard calculations for dependents’/ survivors’ pension, the value of 40% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler methodology for this component.
**Provident Fund and Individual Mandatory Account
*** There is a minor revision in methodology here. The earlier methodology gave a country a score of 0 if survivors’ benefits were means-tested. Although this condition was in line with Part X of Convention No. 102, this conditionality has now been removed, and scores are adjusted for the following countries:
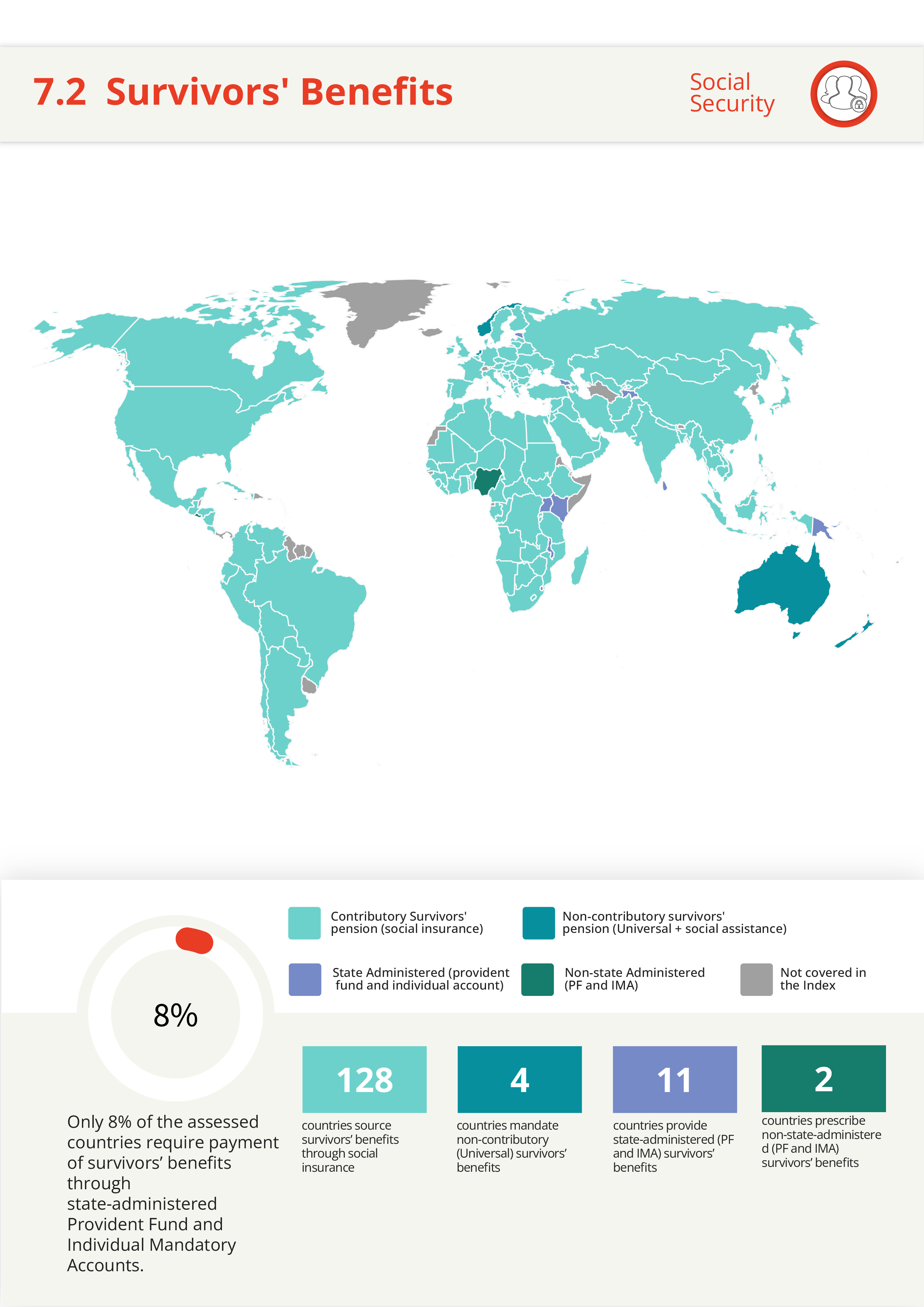
7.3 Unemployment Benefits
Does the law provide for unemployment benefits?
International Regulatory Standard:
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
Article 67 of the ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of unemployment benefits at the rate of at least 45 percent of a worker’s former wage, where the contingency covered should include earnings’ suspension as defined by national laws or regulations, due to inability to obtain suitable employment in the case of a person protected who is capable of, and available for, work. The minimum duration of the benefit shall be a periodical payment for 13 weeks in a period of 12 months or periodic payment for 26 weeks within 12 months where all residents whose means during the contingency do not exceed prescribed limits.
Scoring Methodology:
Whether the legislation provides for unemployment benefits:
1: The legislation provides for unemployment benefits, when a worker loses employment, either through a contributory social insurance system or a noncontributory universal benefits system. *
0: There is no explicit provision for a state-administered unemployment benefits system or where only severance pay is provided in the event of unemployment.
*Due to varying standards, the value of 45% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler methodology for this component.
There is a minor revision in methodology here. The earlier methodology gave a country a score of 0 if unemployment benefits were means-tested. Although this condition was in line with Part IV of Convention No. 102, this conditionality has now been removed, and scores are adjusted for the following countries.
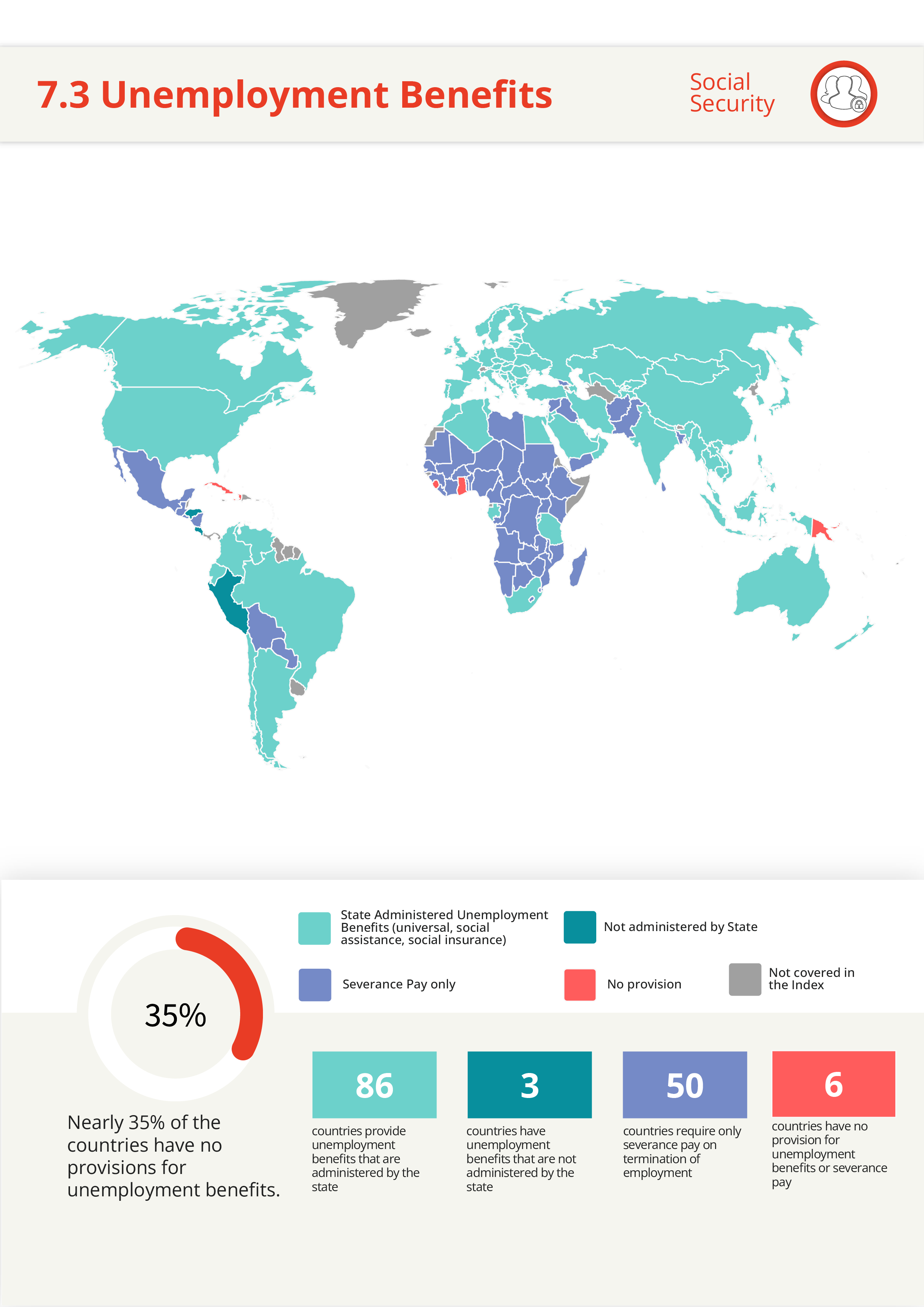
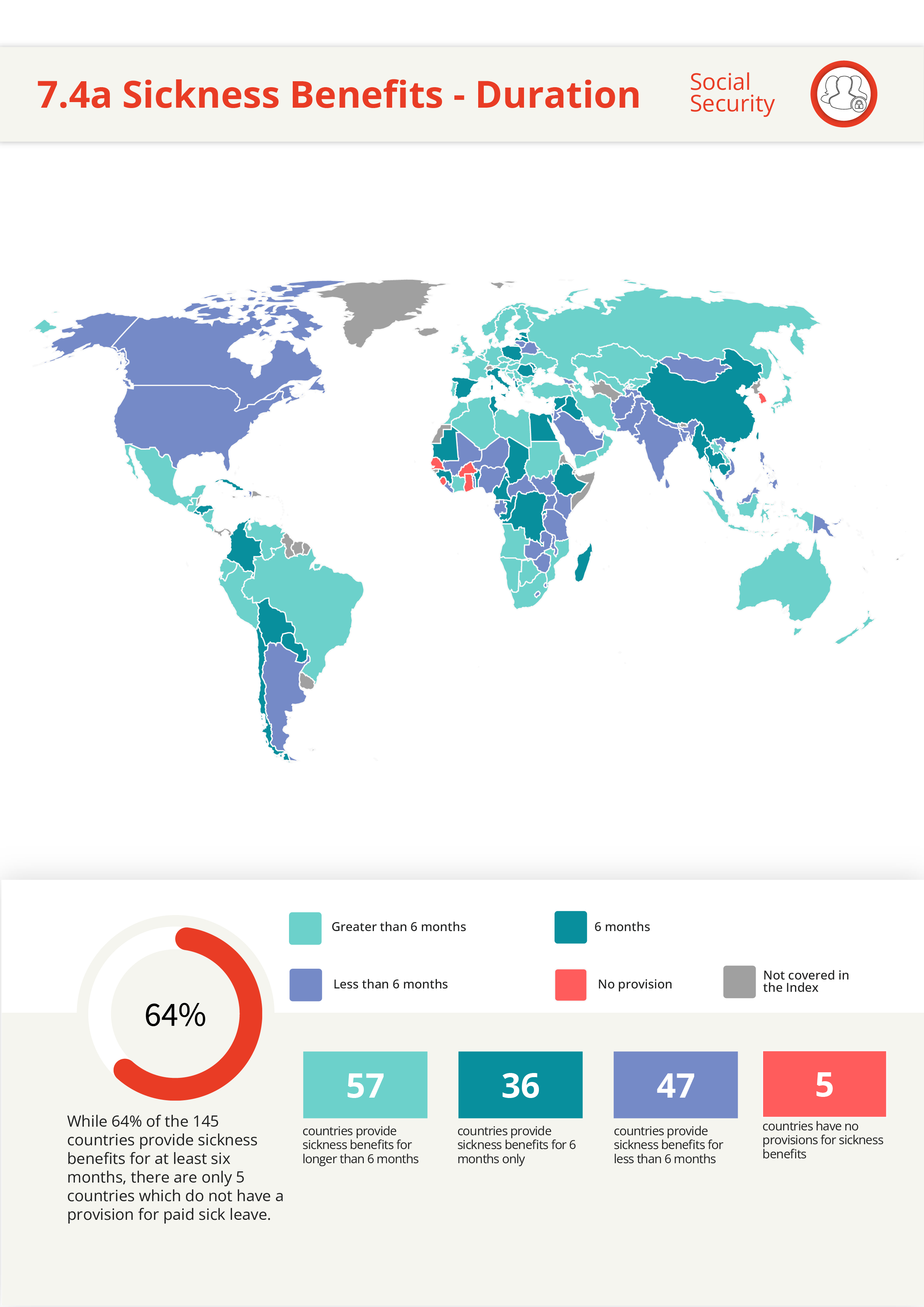
7.4a Sickness Benefits - Duration
Does the law require paid sick leave (and sickness benefits) for the first six months of sickness?
International Regulatory Standard
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
Article 67 of the ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of sickness benefits at the rate of at least 45 percent of a worker’s former wage, where the contingency covered should include incapacity for work resulting from a morbid condition and involving suspension of earnings, as defined by national laws or regulations. The benefit shall be a periodic payment for the whole of the contingency and limited to 26 weeks in each case of sickness, in which event it need not be paid for the first three days of suspension of earnings.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the legislation provides for paid sick leave for the first six months of sickness:
1: The legislation allows paid sick leave or sickness benefits for a minimum of the first six months of illness. The paid sick leave/sickness benefits must have been funded through a contributory social insurance system or a universally accessible system.*
0: The duration of paid sick leave/sickness benefits is less than six months or if the paid sick leave is only employer liability.
*Due to varying standards, the value of 45% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler methodology for this component.
*** There is a minor revision in methodology here. The earlier methodology gave a country a score of 0 if sickness benefits were means-tested. Although this condition was in line with Part III of Convention No. 102, this conditionality has now been removed. The earlier methodology also gave a score of 0 if the waiting period (before payment of sickness benefits by the social security system) exceeded 10 days. This conditionality has also dropped since longer waiting periods were found for those countries where the length of sickness benefits is longer than six months. Scores are adjusted for the following countries:
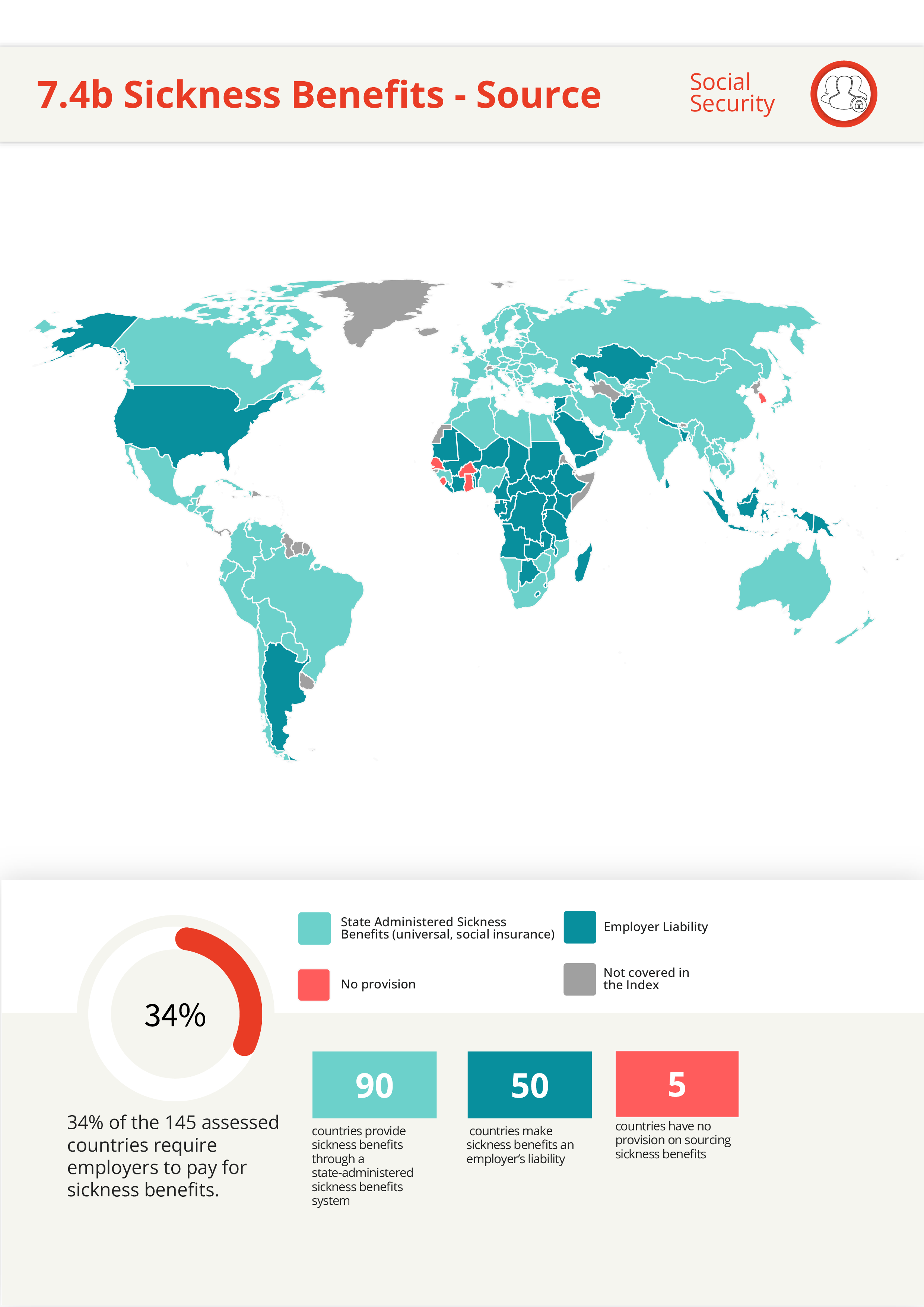
7.4b Sickness Benefits - Source
Does the law require paid sick leave (and sickness benefits) for the first six months of sickness?
International Regulatory Standard
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
Article 67 of the ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of sickness benefits at the rate of at least 45 percent of a worker’s former wage, where the contingency covered should include incapacity for work resulting from a morbid condition and involving suspension of earnings, as defined by national laws or regulations. The benefit shall be a periodic payment for the whole of the contingency and limited to 26 weeks in each case of sickness, in which event it need not be paid for the first three days of suspension of earnings.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the legislation provides for paid sick leave for the first six months of sickness:
1: The legislation allows paid sick leave or sickness benefits for a minimum of the first six months of illness. The paid sick leave/sickness benefits must have been funded through a contributory social insurance system or a universally accessible system.*
0: The duration of paid sick leave/sickness benefits is less than six months or if the paid sick leave is only employer liability.
*Due to varying standards, the value of 45% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler methodology for this component.
*** There is a minor revision in methodology here. The earlier methodology gave a country a score of 0 if sickness benefits were means-tested. Although this condition was in line with Part III of Convention No. 102, this conditionality has now been removed. The earlier methodology also gave a score of 0 if the waiting period (before payment of sickness benefits by the social security system) exceeded 10 days. This conditionality has also dropped since longer waiting periods were found for those countries where the length of sickness benefits is longer than six months. Scores are adjusted for the following countries:
Albania, Australia, Austria
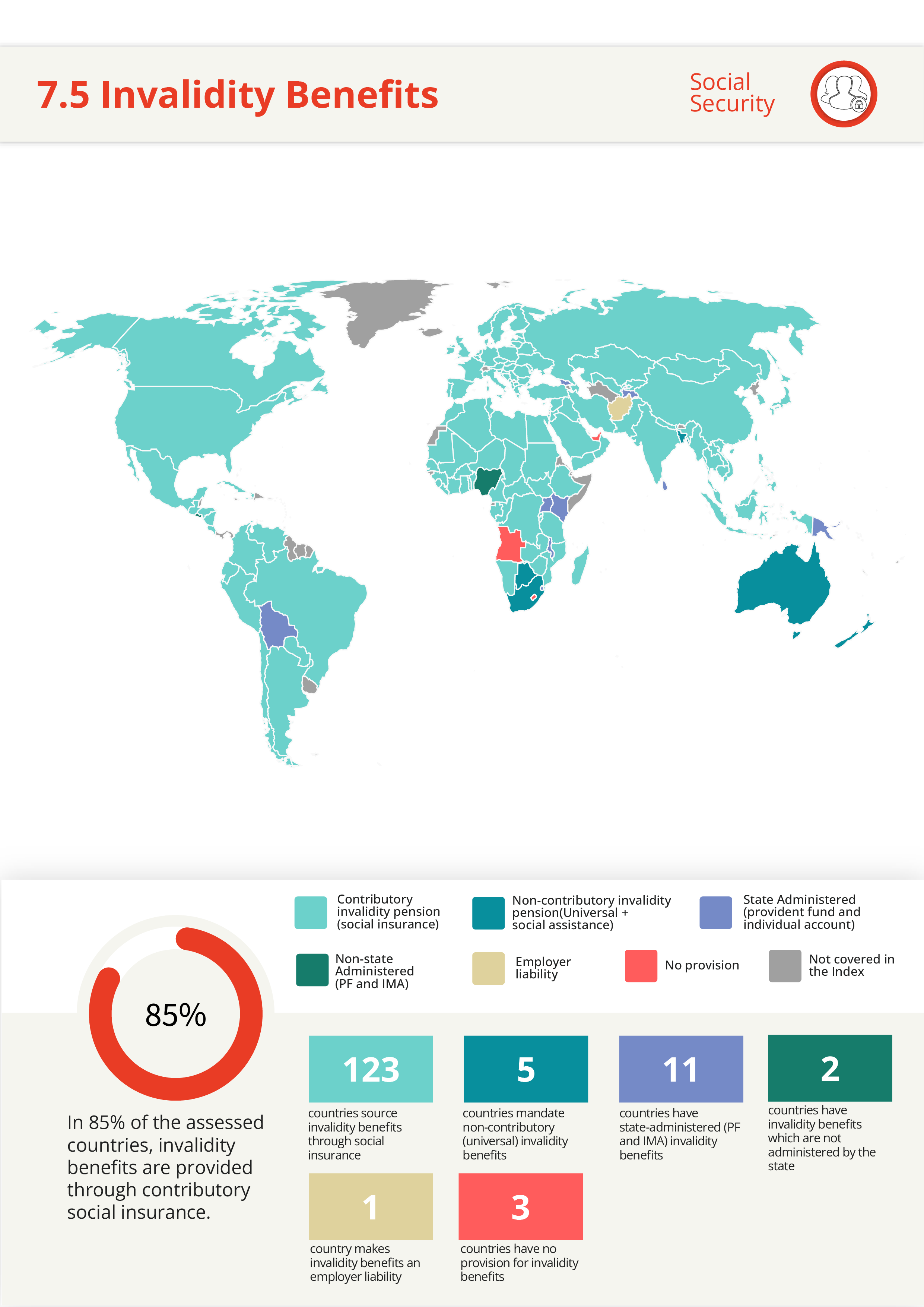
7.5 Invalidity Benefits
Does the law provide for invalidity benefits?
International Regulatory Standard
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
Article 67 of the ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of invalidity benefit at the rate of 40 per cent of a worker’s former wage, where the contingency covered shall include the inability to engage in any gainful activity to an extent prescribed which inability is likely to be permanent or persists after the exhaustion of sickness benefit. The benefit shall be a periodical payment, and it shall be granted throughout the contingency or until an old-age benefit becomes payable.
Scoring Methodology
Whether legislation provides for invalidity benefits:
1: Invalidity benefit is provided under the law and is paid through a contributory social insurance system or through a non-contributory universal benefits system financed through general taxation (both administered by the state) or if there is a provision for non- state-administered invalidity benefits.*
0: The invalidity benefit is only an employer’s liability, or if there is no explicit provision for an invalidity benefits system.
*Due to nonstandard calculations for the employee invalidity benefits, the value of 40% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler methodology for this component.
** There is a minor revision in methodology here. The earlier methodology gave a country a score of 0 if invalidity benefits were means-tested. Although this conditionality was in line with Part IX of Convention No. 102, it has now been removed, and scores are adjusted for the following countries:
Social Security - comparative tables
Old Age Benefits
| Region | Contributory Old Age benefits (Social Insurance) | Non- Contributory Survivors’ benefits (Universal + social assistance) | State Administered (Provident Fund & Mandatory Individual Account) | Non-State Administered (PF & MIA) | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | South Africa | Eswatini, Gambia, Kenya, Malawi, Uganda | Nigeria | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | Mexico | El Salvador | 19 | |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Malaysia, Singapore, Sri Lanka | 38 | ||
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | Estonia, Georgia, Norway | 40 | ||
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 127 | 4 | 12 | 2 | 145 |
Dependants’/Survivors’ Benefits
| Region | Contributory Survivors’ benefits (Social Insurance) | Non-Contributory Survivors ’benefits (Universal + social assistance) | State Administered (Provident Fund & Mandatory Individual Account) | Non-State Administered (PF & MIA) | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Eswatini, Gambia, Kenya, Malawi, Uganda | Nigeria | 45 | |
| Americas | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | El Salvador | 19 | ||
| Asia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Taiwan , Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Singapore, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan | 38 | ||
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | Netherlands, Norway | Estonia, Georgia | 40 | |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 128 | 4 | 11 | 2 | 145 |
Unemployment Benefits
| Region | Non-State Administered | State Administered | Severance Pay only | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Egypt, Gabon, Morocco, South Africa, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania | Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gambia, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Ghana, Sierra Leone | 45 | |
| Americas | Costa Rica, Honduras, Peru | Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, United States of America, Venezuela | Bolivia, El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay | Cuba, Haiti | 19 |
| Asia | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Iraq, Lebanon, Pakistan, Qatar, Sri Lanka, Syria, Yemen | Singapore | 38 | |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | Georgia | 40 | ||
| Oceania | New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 3 | 86 | 50 | 6 | 145 |
Sickness Benefit - Duration
| Region | < 6 months | 6 months | > 6 months | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Burundi, Central African Republic, Eswatini, Gabon, Gambia, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Niger, Nigeria, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Benin, Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Guinea, Madagascar, Mauritania, Rwanda, Tunisia | Algeria, Angola, Botswana, Cabo Verde, Côte D'Ivoire, Libya, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, South Africa, Sudan | Burkina Faso, Ghana, Senegal, Sierra Leone | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Canada, Haiti, United States of America | Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Cuba, El Salvador, Honduras, Paraguay | Brazil, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Mexico, Nicaragua, Peru, Venezuela | 19 | |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, India, Israel, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Nepal, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan, United Arab Emirates, Viet Nam | Cambodia, China, Iraq, Myanmar, Syria, Taiwan , Thailand | Azerbaijan, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Oman, Uzbekistan, Yemen | Republic of Korea | 38 |
| Europe | Belarus, Georgia, Lithuania, Montenegro | Albania, Cyprus, Estonia, Italy, Latvia, Malta, Moldova, Poland, Romania, Spain | Austria, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Luxembourg, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Portugal, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | Papua New Guinea | Australia, New Zealand | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 47 | 36 | 57 | 5 | 145 |
Sickness Benefit - Source
| Region | Employer Liability | State Administered Sickness Benefits (Universal, Social insurance) | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Rwanda, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | Algeria, Cabo Verde, Egypt, Guinea, Libya, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa, Tunisia, Zimbabwe | Burkina Faso, Ghana, Senegal, Sierra Leone | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, United States of America | Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, Venezuela | 19 | |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Malaysia, Nepal, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Syria, United Arab Emirates, Yemen | Azerbaijan, Cambodia, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Mongolia, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | Republic of Korea | 38 |
| Europe | Georgia | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | Papua New Guinea | Australia, New Zealand | 3 | |
| Total Countries | 50 | 90 | 5 | 145 |
Invalidity Benefits
| Region | Contributory invalidity benefits (social insurance) | Non-Contributory Invalidity benefits (Universal + social assistance) | State Administered (Provident Fund & Mandatory Individual Account) | Non-State Administered (PF & MIA) | Employer Liability | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Botswana, South Africa | Eswatini, Gambia, Kenya, Malawi, Uganda | Nigeria | Angola, Lesotho | 45 | |
| Americas | Argentina, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | Bolivia | El Salvadore | 19 | |||
| Asia | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Taiwan , Thailand, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Bangladesh | Singapore, Sri Lanka, Tajikistan | Afghanistan | United Arab Emirates | 38 | |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | Georgia | 40 | ||||
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||||
| Total Countries | 123 | 5 | 11 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 145 |
Social Security - country score snapshot