Decent work, in essence, is safe work. The Safe Work indicator measures whether labour legislation ensures that workers are trained about health and safety issues before the commencement of work and whether the employer provides free personal protective equipment to workers. It also measures countries' compliance on restrictions on arduous work for pregnant workers and whether countries provide some kind of employment injury benefits.
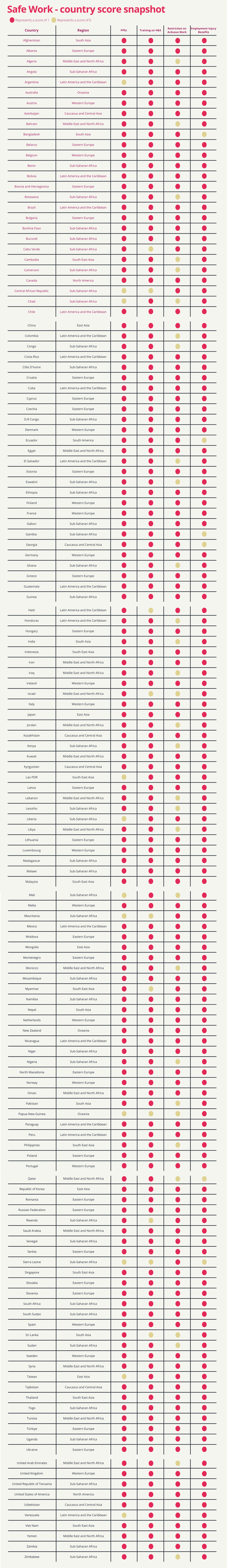
6.1 Free Personal Protective Equipment
Does the law require employers to provide free personal protective equipment to workers?
International Regulatory Standard
- Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981 (No. 155)
- Occupational Safety and Health Recommendation, 1981 (No. 164)
Article 16 of the ILO’s Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981 (No. 155) states that employers shall be required to ensure that, so far as is reasonably practicable, the workplaces, machinery, equipment and processes under their control are safe and without health risk; and that the chemical, physical and biological substances and agents under their control are without health risk when the appropriate measures of protection are taken. Also, the employers shall be required to provide, where necessary, adequate protective clothing and protective equipment to prevent, so far as is reasonably practicable, the risk of accidents or adverse effects on health.
Furthermore, Article 21 of this Convention states that occupational safety and health measures shall not involve any expenditure by the workers. Paragraph 10(e) of the ILO’s Occupational Safety and Health Recommendation, 1981 (No. 164) also requires employers “to provide, without any cost to the worker, adequate personal protective clothing and equipment which are reasonably necessary when hazards cannot be otherwise prevented or controlled”.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law requires employers to provide free personal protective equipment to workers:
1: Labour legislation requires employers to provide free personal protective equipment to the workers.
0: There is no requirement to provide free personal protective equipment to workers
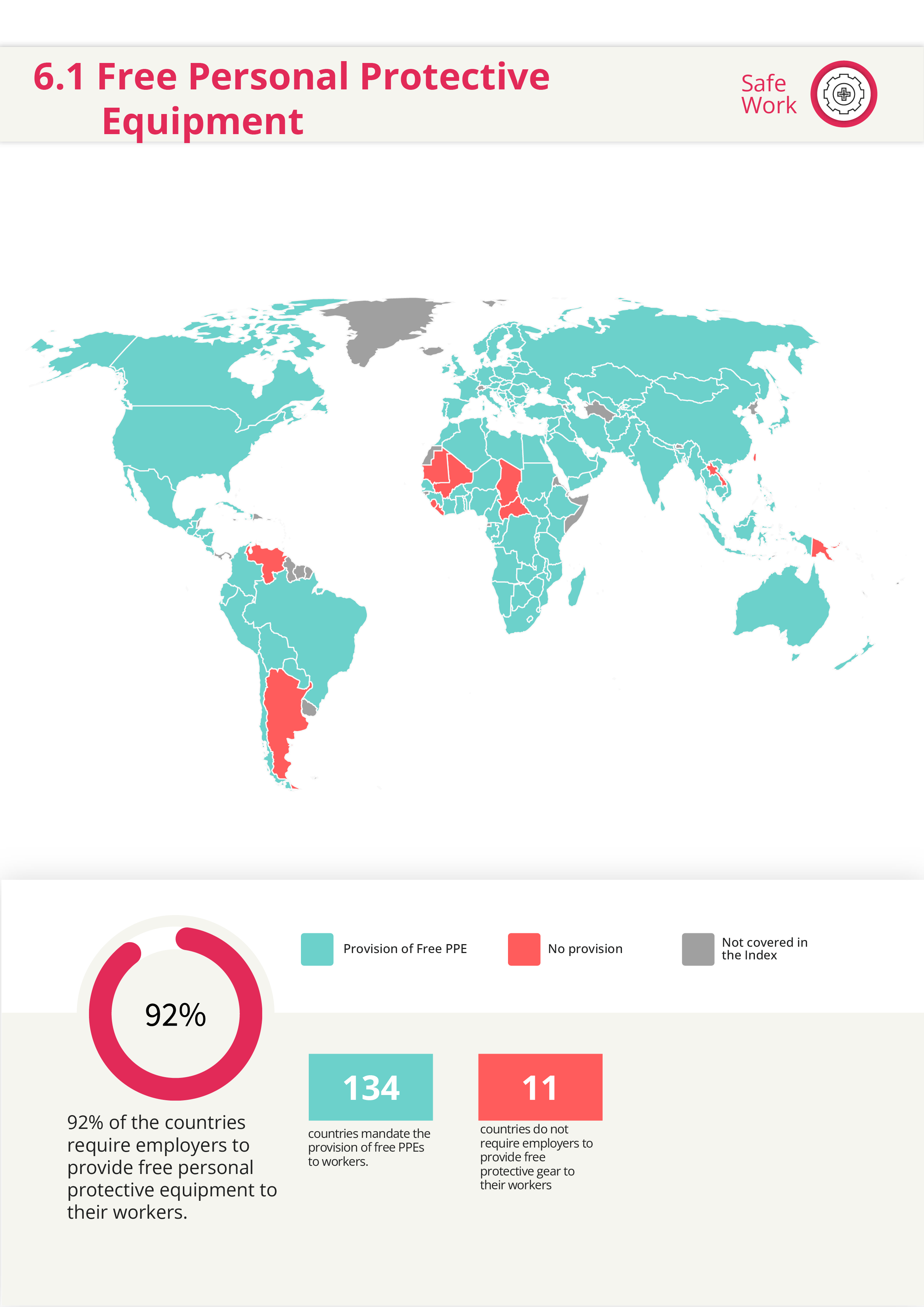
6.2 Training - Occupational Safety and Health
Does the law require employers to train workers on health and safety Issues?
International Regulatory Standard
- Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981 (No. 155)
- Occupational Safety and Health Recommendation, 1981 (No. 164)
Article 19(d) of the ILO’s Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981 (No. 155) requires that there should be arrangements at the level of the undertaking/enterprise under which workers and their representatives in the workplace are given appropriate training in occupational safety and health.
Paragraph 10(b) of the ILO’s Occupational Safety and Health Recommendation, 1981 (No. 164) requires employers to give necessary instructions and training, taking account of the functions and capacities of different categories of workers.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the legislation requires employers to train workers on health and safety issues:
1: The law requires employers to provide health and safety training to workers when they join work or are assigned new work.
0: The legislation does not require employers to provide training to workers on health and safety issues.
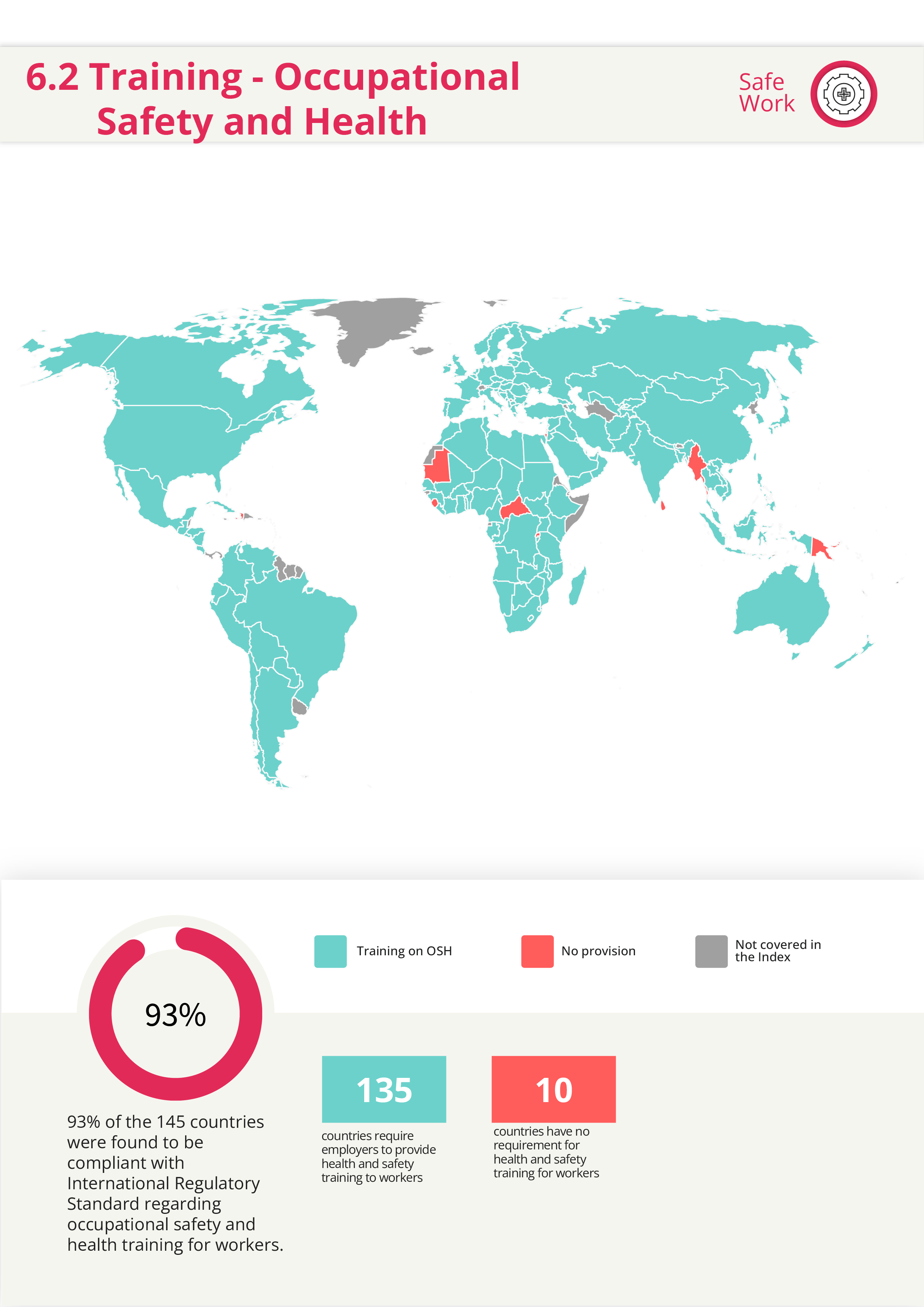
6.3 Restrictions on Work (for Pregnant or Nursing Women)
Does the law restrict work that is prejudicial to the health of the mother or the child?
International Regulatory Standard
- Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183)
- Maternity Protection Recommendation, 2000 (No. 191)
From the ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183), Article 3 states that after consulting the representative organisations of employers and workers, appropriate measures should be adopted to ensure that pregnant or breastfeeding women are not obliged to perform work which has been determined by the competent authority to be prejudicial to the health of the mother or the child, or where an assessment has established a significant risk to the mother’s health or that of her child.
Detailed provisions on health protection of a pregnant or nursing woman and her child are found in Paragraph 6 of the ILO’s Maternity Protection Recommendation, 2000 (No. 191).
Scoring Methodology
Whether the legislation restricts work that is determined to be prejudicial to the health of the mother or the child:
1: The legislation restricts pregnant or nursing women from being obliged to perform arduous work and night work that is prejudicial to the health of the mother or the child. Based on the workplace assessment and medical certificate, legislation should require the elimination of risk, adaptation of working conditions, transfer to another post without loss of pay, and access to paid leave when neither of the above is possible.
0: Arduous work and any of its other forms* are not prohibited for pregnant or nursing workers, or there is a general prohibition only.
*As noted in Paragraph 6(3) of the ILO Recommendation 191
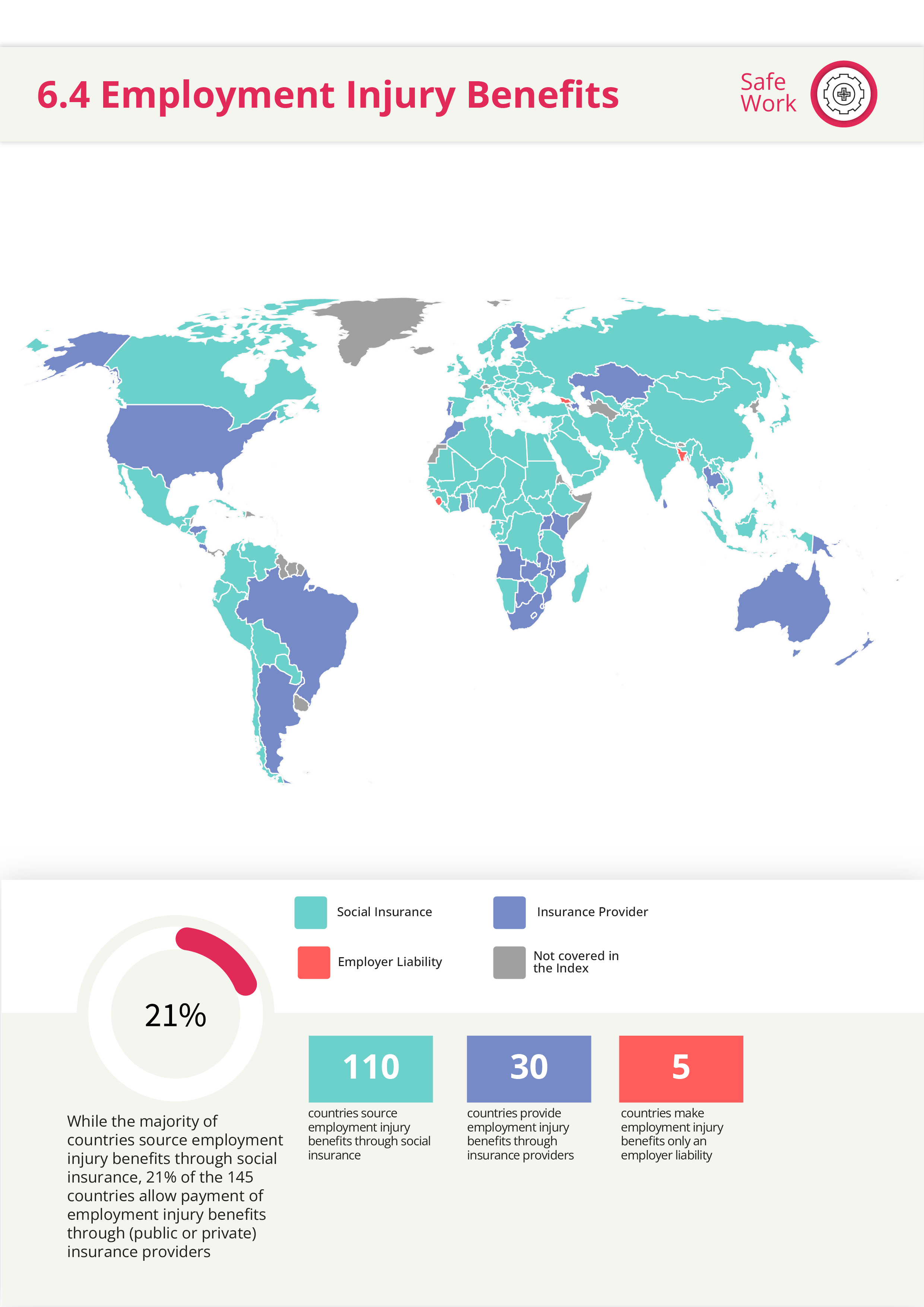
6.4 Employment Injury Benefits
Does the law provide for employment injury benefits in the event of an occupational accident or disease?
International Regulatory Standard
- Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102)
ILO’s Social Security (Minimum Standards) Convention, 1952 (No. 102) stipulates the provision of employment injury benefits at the rate of at least 50 percent of a worker’s former wage (40 percent for survivors).
This applies to an accident or disease resulting from employment, and the contingencies should cover a morbid condition; incapacity for work resulting from such a condition and involving suspension of earnings, as defined by national laws or regulations; total loss of earning capacity or partial loss thereof in excess of a prescribed degree, likely to be permanent, or corresponding loss of faculty; and the loss of support suffered by the widow or child as the result of the death of the breadwinner. In the case of a widow, the right to benefit may be made conditional on her being presumed, in accordance with national laws or regulations, to be incapable of self-support.*
Scoring Methodology
Whether legislation provides for employment injury benefits:
1: Employment injury benefits (in case of occupational accident or disease) are provided under the law and are paid through social insurance, or the employer pays a monthly premium to the private or public carrier (insurance provider) to provide employment injury benefits.
0: Employment injury benefits are not financed through the social insurance system or public or private carrier (is employer liability program only) or is not provided under the law.
*Due to nonstandard calculations for employee injury benefits, the value of 50% and 40% cannot be easily ascertained for countries. This led to the use of a simpler scoring Scoring Methodology for this component.
Safe Work - comparative tables
Free Personal Protective Equipment
| Region | Provision of Free PPE | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Central African Republic, Chad, Liberia, Mali, Mauritania, Sierra Leone | 45 |
| Americas | Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America | Argentina, Venezuela | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Syria, Tajikistan, Thailand, United Araba Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Lao People's Democratic Republic, Taiwan | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 |
| Total Countries | 134 | 11 | 145 |
Training on OSH
| Region | Training on OSH | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Central African Republic, Cabo Verde, Rwanda, Mauritania, Sierra Leone | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | Haiti | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Araba Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Israel, Myanmar, Sri Lanka | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 |
| Total Countries | 135 | 10 | 145 |
Restriction on Work (for Pregnant or Nursing Women)
| Region | Prohibition of Work Prejudicial to the Health of Mother or Child | No Prohibition | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Central African Republic, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Guinea, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | Algeria, Botswana, Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Eswatini, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Libya, Mali, Morocco, Nigeria, Sudan, Zimbabwe | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, Guatemala, Haiti, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | Colombia, El Salvador, Honduras | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bangladesh, China, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Bahrain, Cambodia, India, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Sri Lanka, United Arab Emirates | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 |
| Total Countries | 114 | 31 | 145 |
Employment Injury Benefits
| Region | Employer Liability | Insurance Provider | Social Insurance | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Gambia, Sierra Leone | Angola, Botswana, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Eswatini, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Malawi, Morocco, Mozambique, South Africa, Uganda, Zambia | Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Guinea, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania, Zimbabwe | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Brazil, Costa Rica, Honduras, United States of America | Bolivia, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, Venezuela | 19 | |
| Asia | Bangladesh, Qatar | Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Lebanon, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand | Afghanistan, Bahrain, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | 38 |
| Europe | Georgia | Finland, Portugal | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 5 | 30 | 110 | 145 |
Safe Work - country score snapshot