Maternity protection allows women to successfully combine their productive and reproductive roles without compromising one at the cost of another. Similarly, it protects women from discrimination in the labour market due to their reproductive roles. The Maternity at Work indicator measures whether labour legislation ensures that workers get paid maternity leave and are protected from dismissal during and on account of pregnancy.
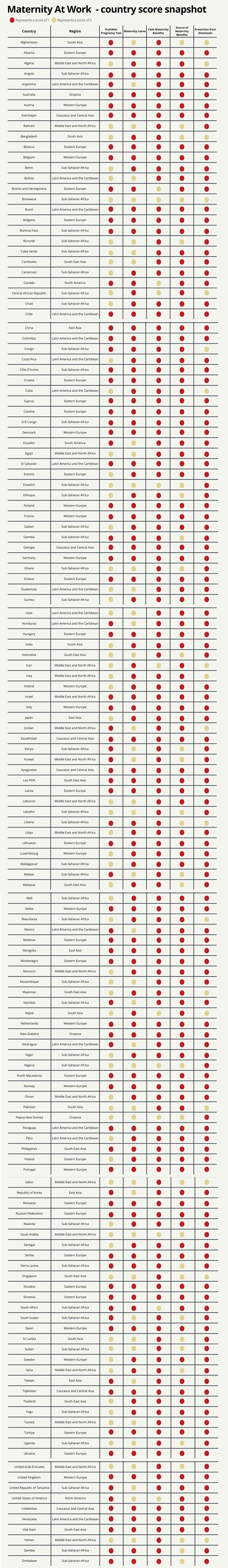
5.1 Pregnancy Inquiry During Recruitment
Does the law prohibit inquiring about pregnancy during recruitment?
International Regulatory Standard
- Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183)
Article 9 of the ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183) focuses on adopting appropriate measures to ensure that maternity does not constitute a source of discrimination in employment, including access to employment. Measures need to include a prohibition from requiring a test for pregnancy or a certificate of such a test when a woman is applying for employment, except where required by national laws or regulations in respect of work that is prohibited or restricted for pregnant or nursing women under national laws or regulations, or where there is a recognised or significant risk to the health of the woman and child.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law prohibits inquiring about pregnancy during recruitment:
1: Labour legislation prohibits employers from inquiring about pregnancy (through pregnancy testing or other means) during recruitment.
0: There is no prohibition in the law on inquiring about pregnancy/family planning during recruitment or making it a recruitment condition.
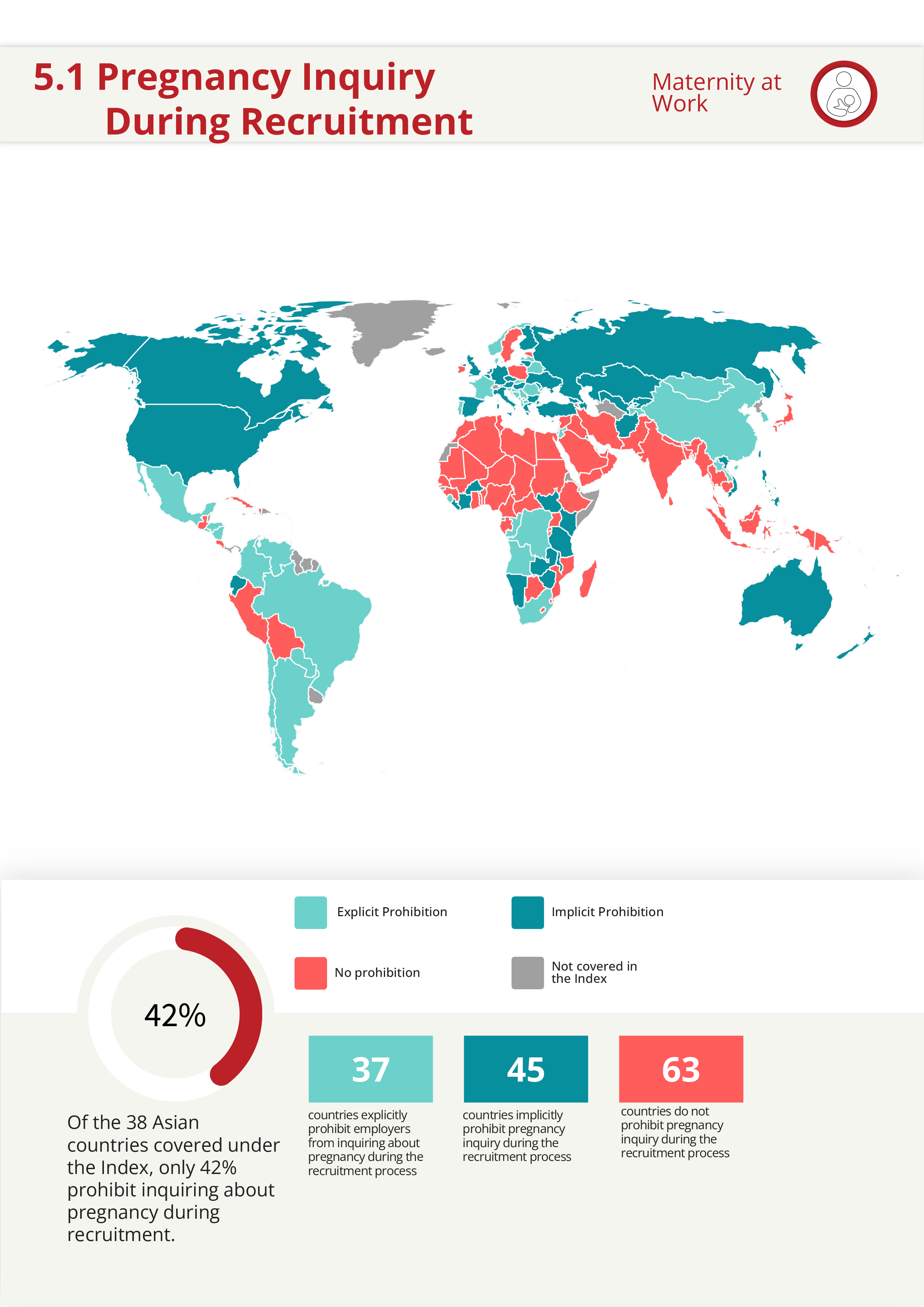
5.2 Maternity Leave
Does the law require maternity leave of at least 14 weeks?
International Regulatory Standard
- Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183)
Article 4 of the ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183) stipulates that a woman worker shall be entitled to a maternity leave of at least 14 weeks. With due regard to the protection of the mother's and child's health, maternity leave shall include a period of six weeks of compulsory leave after childbirth unless otherwise agreed at the national level by the government and the representative organisations of employers and workers.
Scoring Methodology
Whether maternity leave is available for at least 14 weeks:
1: Women workers have the right to maternity leave of at least 14 weeks.
0: The length of maternity leave is less than 14 weeks.
5.3 Maternity Benefits
Does the law require cash maternity benefits to be at least two-thirds (66.67%) of a worker's former wage?
International Regulatory Standard
- Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183)
Article 6 of the ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183) shares that cash benefits shall be provided, in accordance with national laws and regulations, or in any other manner consistent with the national practice, to women who are absent from work on leave. The maternity benefits shall be set at a level that ensures that the woman can maintain proper health and a suitable standard of living for herself and her child. The amount of such benefits, however, shall not be less than two-thirds of the woman’s previous earnings or of such of those earnings as are taken into account for the purpose of computing benefits.
Scoring Methodology
Whether cash maternity benefit is at least two-thirds of the worker’s former wage:
1: Maternity benefit is two-thirds or higher than the pregnant worker’s former wage. In cases where the maternity leave is over and above 14 weeks, the score will remain 1 if the payment for maternity leave through social insurance or universal benefits is at least two-thirds of the former wage for at least the first 14 weeks. In cases where workers are paid flat-rate maternity benefits, these must be at least two-thirds of the applicable minimum wage in the country.*
0: Maternity leave benefit is less than the above threshold (two-thirds of the woman worker’s previous earnings).
*The length of 14 weeks was set after an extensive review of national legislation. It allows a cross-country comparison.

5.4 Source of Maternity Benefits
Does the law require cash maternity benefits to be paid through a contributory social insurance or a universal benefits system or such benefits are an employer's liability?
International Regulatory Standard
- Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183)
Article 6(8) of the ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183) states that to protect the situation of women in the labour market, benefits in respect of the leave shall be provided through compulsory social insurance or public funds or in a manner determined by national law and practice. The employers shall not be individually liable for the direct cost of any such monetary benefit to a woman employed by them without that employers’ specific agreement except where such benefit is provided for in national law prior to the introduction of this Convention, or it is subsequently agreed at the national level by the government and the representative organisations of employers and workers.
Scoring Methodology
Whether cash maternity benefits are an employer’s liability:
1: Maternity benefits are paid through a contributory social insurance system or through a non-contributory universal benefits system financed through general taxation.
0: Maternity benefits are only employer liability, and employers are required to pay workers their wages during maternity leave.

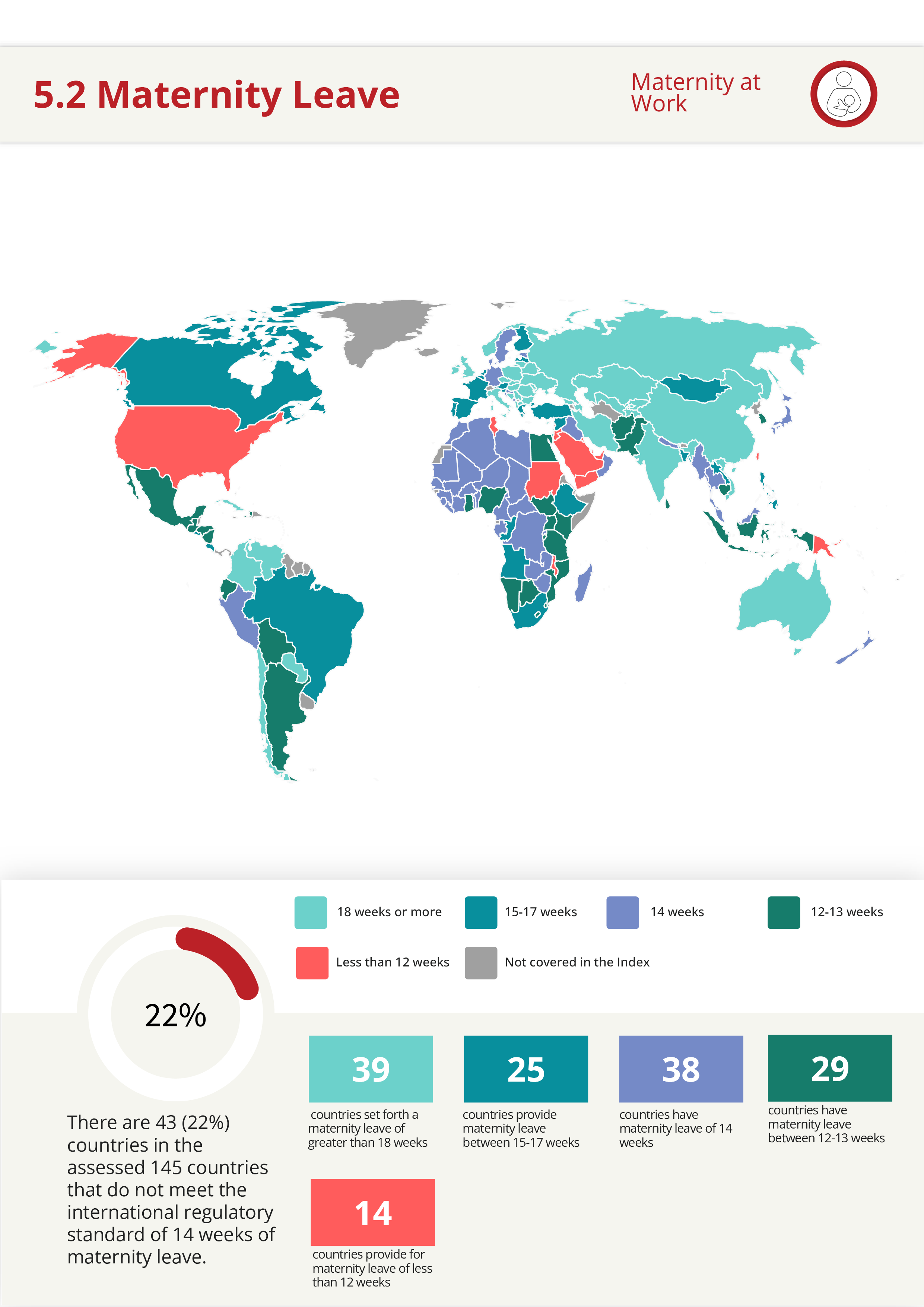
5.5 Dismissals During Pregnancy
Does the law protect workers from dismissals during or on account of pregnancy?
International Regulatory Standard
- Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183)
Article 8 of the ILO’s Maternity Protection Convention, 2000 (No. 183) stipulates that it is unlawful for an employer to terminate the employment of a woman during her pregnancy or absence on leave or during a period following her return to work, except on grounds unrelated to the pregnancy or birth of the child and its consequences or nursing.
Moreover, a woman is guaranteed the right to return to the same position or an equivalent position paid at the same rate at the end of her maternity leave.
Article 11 (2) (a) of the UN Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women, 1979 (CEDAW) states that to prevent discrimination against women on the grounds of marriage or maternity and to ensure their effective right to work, appropriate measures should be taken. This includes the prohibition on, subject to the imposition of sanctions, dismissal on the grounds of pregnancy or of maternity leave and discrimination in dismissals based on marital status.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the legislation protects workers from dismissal during or on account of pregnancy:
1: The legislation prohibits employers from terminating workers during or on account of pregnancy (e.g., medically certified sickness related to pregnancy) except in cases of gross misconduct.
0: The legislation does not protect workers from being dismissed during or on account of pregnancy.
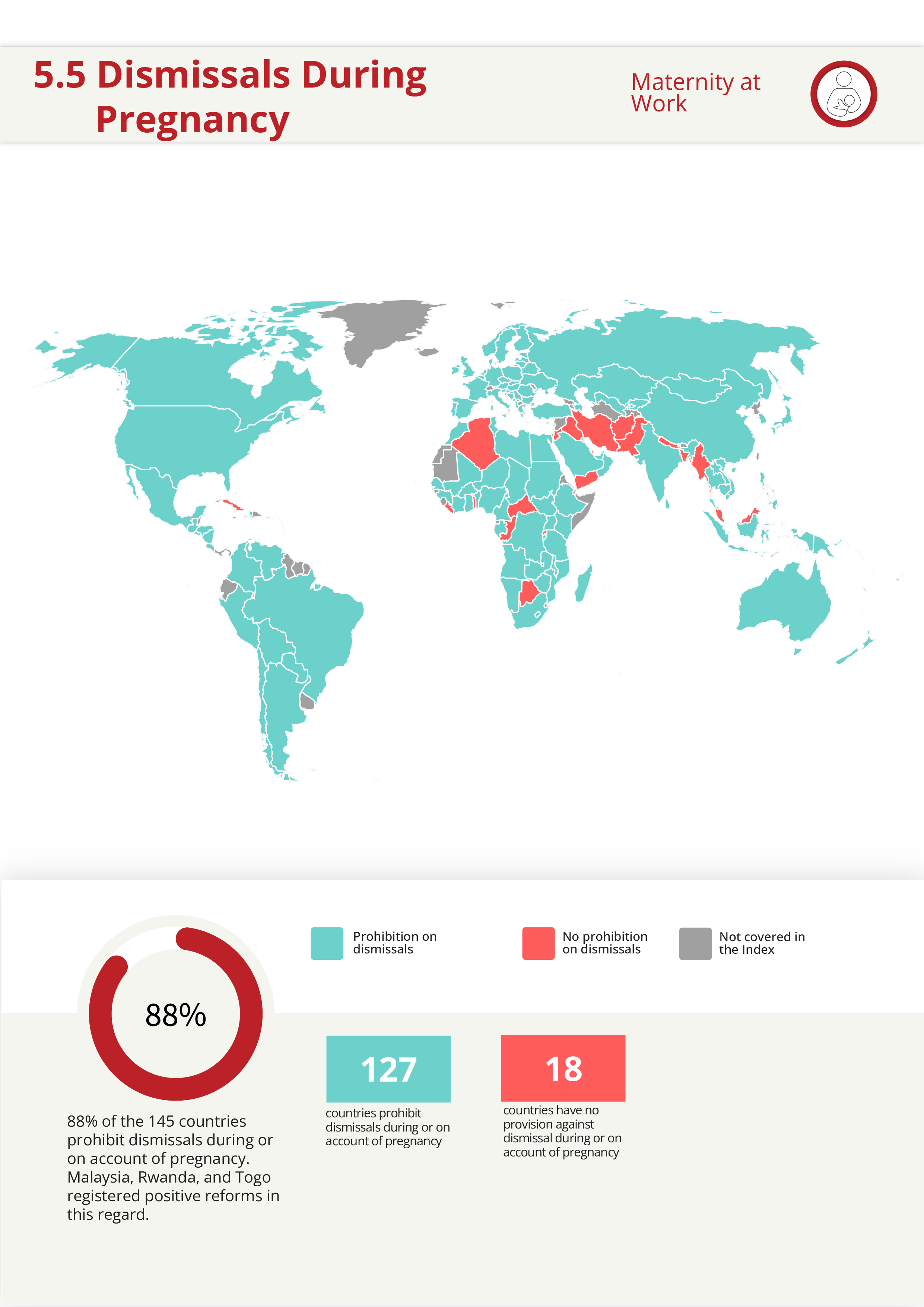
Maternity at Work - comparative tables
Pregnancy Inquiry during Recruitment
| Region | Explicit Prohibition | Implicit Prohibition | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Sierra Leone, South Africa | Burkina Faso, Côte D'Ivoire, Gambia, Kenya, Liberia, Malawi, Namibia, South Sudan, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Algeria, Benin, Botswana, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, El Salvador, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Venezuela | Canada, Ecuador, United States of America | Bolivia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Guatemala, Haiti, Peru | 19 |
| Asia | China, Israel, Jordan, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Mongolia, Republic of Korea, Tajikistan | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Philippines, Taiwan , Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Japan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Syria, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Yemen | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Denmark, France, Latvia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Norway, Portugal, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia | Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czechia, Finland, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Lithuania, Malta, Moldova, Netherlands, Russian Federation, Spain, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | Estonia, Ireland, Luxembourg, Poland, Sweden | 40 |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | |
| Total Countries | 37 | 45 | 63 | 145 |
Maternity Leave
| Region | < 12 Weeks | 12-13 Weeks | 14 Weeks | 15-17 Weeks | ≥ 18 Weeks | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Malawi, Sudan, Tunisia | Botswana, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Egypt, Eswatini, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Mozambique, Namibia, Nigeria, South Sudan, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania | Algeria, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Guinea, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, Togo, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Angola, Congo, Ethiopia, South Africa | Gambia | 45 |
| Americas | United States of America | Argentina, Bolivia, Ecuador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua | Peru | Brazil, Canada, Costa Rica, El Salvador | Chile, Colombia, Cuba, Paraguay, Venezuela | 19 |
| Asia | Bahrain, Jordan, Kuwait, Lebanon, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Taiwan , United Arab Emirates, Yemen | Afghanistan, Cambodia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Republic of Korea, Singapore, Sri Lanka | Iraq, Japan, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Thailand | Bangladesh, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Mongolia, Philippines, Syria | Azerbaijan, China, India, Iran, Israel, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | 38 |
| Europe | Croatia, Denmark, Estonia, Germany, Montenegro, Sweden | Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Greece, Latvia, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Portugal, Slovenia, Spain, Türkiye | Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Czechia, Georgia, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Lithuania, Malta, Moldova, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | ||
| Oceania | Papua New Guinea | New Zealand | Australia | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 14 | 29 | 38 | 25 | 39 | 145 |
Maternity Benefits
| Region | < 66.67% | ≥ 66.67% | Flat-rate benefit | Unpaid | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Botswana, Central African Republic, Eswatini, Nigeria, South Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | 45 | ||
| Americas | Canada, United States of America | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, Venezuela | 19 | ||
| Asia | Iran, Nepal, Saudi Arabia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Kyrgyz Republic | 38 | |
| Europe | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine | Finland, Georgia, Ireland, Malta, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | New Zealand | Australia | Papua New Guinea | 3 | |
| Total Countries | 11 | 126 | 7 | 1 | 145 |
Source of Maternity Benefits
| Region | Employer Liability | Mixed System | Social Insurance or Universal Benefits | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Botswana, Burundi, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Nigeria, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Sudan, Uganda, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Chad, Congo, Guinea, Madagascar, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Gabon, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Senegal, South Africa, Togo, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania | 45 | |
| Americas | Ecuador, Honduras, Nicaragua | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Mexico, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | 19 | ||
| Asia | Bahrain, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Kuwait, Malaysia, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Syria, United Arab Emirates, Yemen | Nepal, Pakistan, Thailand | Azerbaijan, Cambodia, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Mongolia, Myanmar, Oman, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Uzbekistan | 38 | |
| Europe | Denmark | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | ||
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 30 | 14 | 100 | 1 | 145 |
Prohibition on Dismissals during Pregnancy
| Region | No Prohibition | Prohibition on dismissals | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Botswana, Central African Republic, Congo, Liberia, Mauritania | Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Chad, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | 45 |
| Americas | Cuba | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Qatar, Singapore, Yemen | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Israel, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Oman, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea | 3 | |
| Total Countries | 18 | 127 | 145 |
Maternity At Work - country score snapshot