The Fair Treatment indicator measures legislation causing wage gap, discrimination in employment matters, sexual harassment at work, employment segregation and unequal access to basic labour protection for gig workers. Equal remuneration for all workers, referring to the rates of remuneration without discrimination based on gender and any other discriminatory grounds is the fundamental requirement for promoting non-discrimination at the workplace.
8.1 Equal Remuneration
Does the law require equal remuneration for men and women workers for work of equal value?
International Regulatory Standard
- Equal Remuneration Convention, 1951 (No. 100)
Article 2 of the ILO’s Equal Remuneration Convention, 1951 (No. 100) stipulates that the principle of equal remuneration for men and women workers for work of equal value should be promoted and ensured for all workers by means appropriate to the methods in operation for determining rates of remuneration. This principle may be applied through national laws or regulations, legally established or recognised machinery for wage determination, collective agreements between employers and workers, or a combination of these various means.
The principle of equal remuneration is applied through objective appraisal of jobs on the basis of the work to be performed. The Convention further states that the “differential rates between workers which correspond, without regard to sex, to differences, as determined by such objective appraisal, in the work to be performed shall not be considered as being contrary to the principle of equal remuneration for men and women workers for work of equal value”.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law requires equal remuneration for work of equal value:
1: The legislation mandates equal remuneration for male and female workers for work of equal value without discrimination on the grounds of sex.
0: The law limits the principle of equal remuneration to the same work, similar work, equal work or work of a similar nature, or there is a general prohibition for discrimination in wages or the labour legislation does not even address this issue.
8.2 Sexual Harassment in Employment
Does the law prohibit sexual harassment in employment?
International Regulatory Standard
- Violence and Harassment Convention, 2019 (No. 190)
Article 7 of the ILO’s Violence and Harassment Convention, 2019 (No. 190) states that without prejudice to and consistent with Article 1 (definitions of violence and harassment as well as gender-based violence and harassment), each Member shall adopt laws and regulations to define and prohibit violence and harassment in the world of work, including gender-based violence and harassment. Article 10 of the Convention suggests that members may impose sanctions, where appropriate, in cases of violence and harassment in the world of work.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law prohibits sexual harassment at work:
1: The legislation protects against workplace sexual harassment, with criminal penalties (either fines or imprisonment) or civil remedies (monetary compensation for victims and recovery of damages) or a combination of both.
0: There is no prohibition of sexual harassment in legislation or if the legislation addresses workplace sexual harassment in general terms and has a general prohibition on harassment only.
8.3 Discrimination in Employment
Does the law prohibit discrimination in employment matters?
International Regulatory Standard
- Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention, 1958 (No. 111)
- Vocational Rehabilitation and Employment (Disabled Persons) Convention, 1983 (No. 159)
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities, 2006 (CPRD)
- Right to Organise and Collective Bargaining Convention, 1949 (No. 98)
Article 2 of the Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention, 1958 (No. 111) states that equality of opportunity and treatment in respect of employment and occupation, with the purpose of eliminating any discrimination, should be promoted.
This regulatory standard is based on four different conventions.
The ten prohibited grounds for discrimination are:
- ILO Convention No. 111: race, colour, sex, religion, political opinion, national extraction or social origin, age
- ILO Convention No. 159 and CRPD: disability
- ILO Convention No. 98 : trade union membership or participation in trade union activities
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law prohibits discrimination in employment:
1: The law prohibits employers from engaging in discrimination or mandates equal treatment of all workers in employment matters. A score of 1 is assigned only if a country has prohibited discrimination on at least seven of the following ten grounds. The prohibited grounds for discrimination are “race, colour, sex, religion, political opinion, national extraction or social origin, age, disability and trade union membership".
0: The law does not prohibit such discrimination on at least seven of the ten grounds or only prohibits such discrimination in one or limited aspects of employment, such as pay or dismissal, instead of all employment related matters.
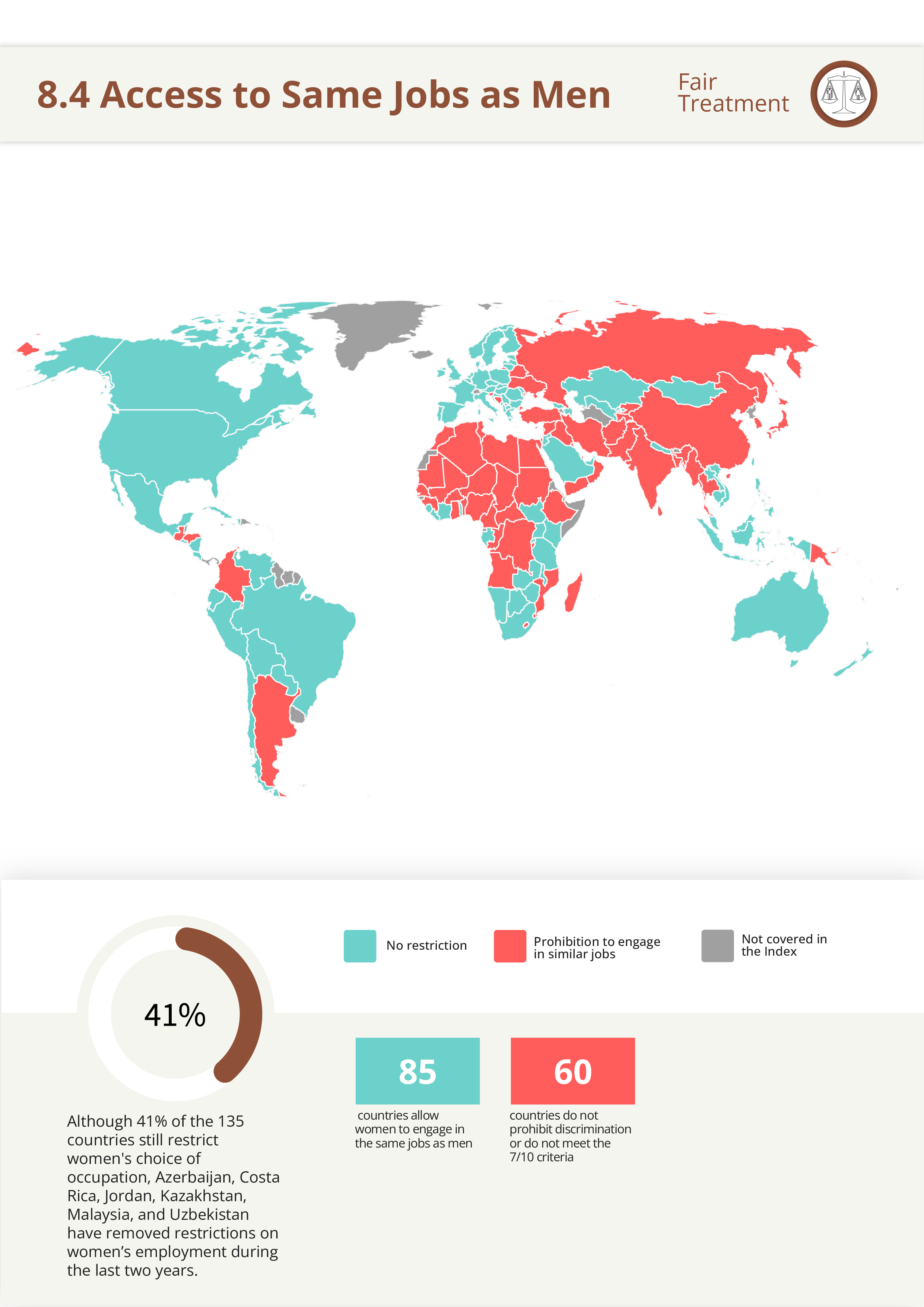
8.4 Access to Same Jobs as Men
Does the law allow women to do the same job as men?
International Regulatory Standard
- Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention, 1958 (No. 111)
Article 2 of the ILO’s Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention, 1958 (No. 111) requires each ratifying Member to declare and pursue a national policy designed to promote, by methods appropriate to national conditions and practice, equality of opportunity and treatment in respect of employment and occupation, and to eliminate any discrimination in respect thereof.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law allows women to do the same jobs as men:
1: The legislation does not restrict non-pregnant and non-nursing women from working in the same jobs as men.
0: The law prohibits or restricts women from working in jobs deemed hazardous, arduous, morally inappropriate and during night hours.
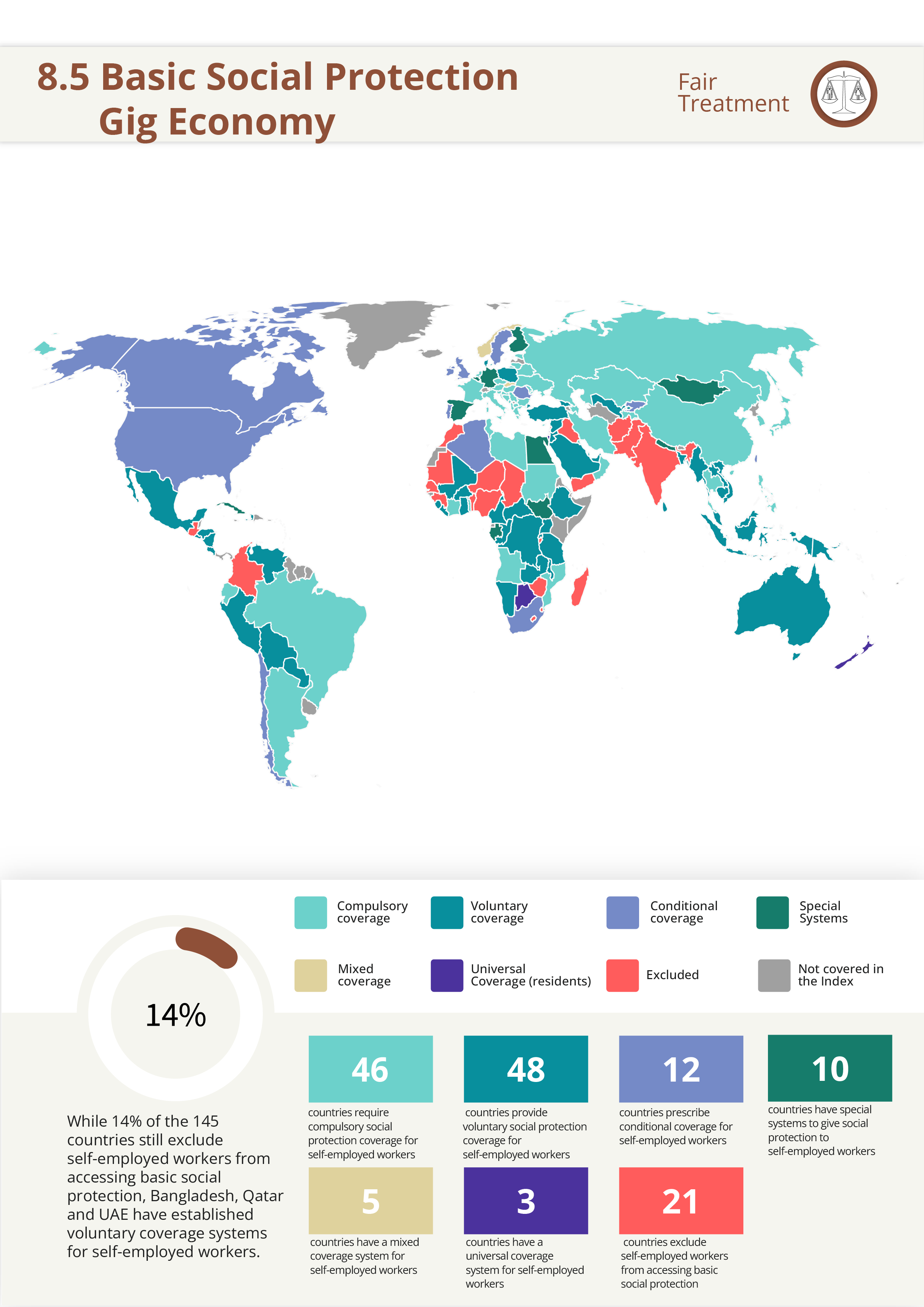
8.5 Basic Social Protection - Platform Economy
Does the law guarantee basic labour protection to the platform workers?
International Regulatory Standard
The Global Commission on the Future of Work 2019 recommended the development of an “international governance system for digital labour platforms”, requiring platforms (and clients) to respect certain minimum rights and protections. The Maritime Labour Convention 2006 (MLC, 2006) can be used as an example.
The ILO Governing Body decided in March 2023 to place on the agenda of the 113th and 114th sessions of the International Labour Conference (June 2025 and 2026), a standard-setting item on decent work in the platform economy. Necessary questionnaires on the form, scope and content of such a standard have been distributed and responses were sought by the social partners and relevant stakeholders.
Similarly, provisions of the Tripartite Declaration of Principles concerning Multinational Enterprises and Social Policy (MNE Declaration) 2017 can be used as guiding principles.
Scoring Methodology
Whether the law guarantees basic labour protection to the platform or gig workers:*
1: Considering the relatively new phenomenon of the platform economy, a score of 1 is currently assigned to all such countries providing access to basic social protection** (old age benefits, survivors’ and invalidity benefits) to self-employed workers.
0: The basic social protection is not afforded to self-employed workers or where access to these benefits is linked to citizenship.
*The basic assumptions of the Index are not applicable to the question on platform work.
**To give equal treatment to workers, labour legislation must regulate the gig or platform economy and provide the following universal labour guarantees or basic labour protections to the platform workers: access to fundamental workers' rights (which inow includes safe and healthy workplaces), social protection, adequate living wages, and decent working hours.
Fair Treatment - comparative tables
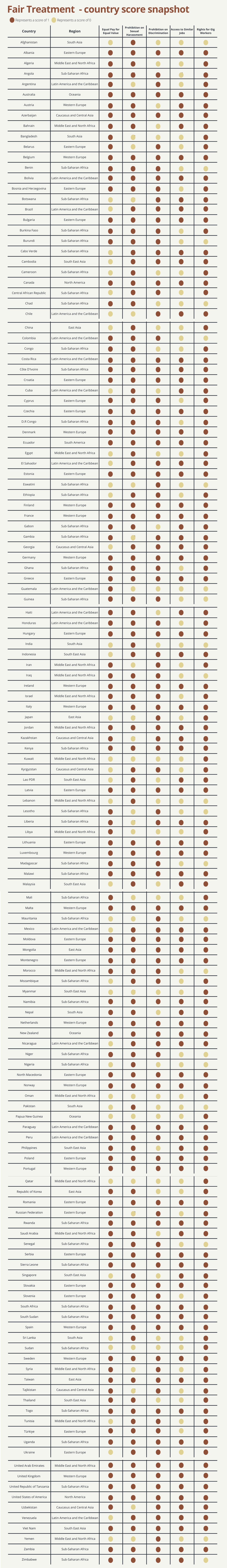
Equal Remuneration
| Region | Equal Remuneration for Work of Equal Value | Equal pay for equal, same or similar work | General prohibition of discrimination in wage matters | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Morocco, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Cameroon, Central African Republic, Eswatini, Mauritania, Mozambique | Cabo Verde, Ethiopia, Tunisia | Botswana, Egypt, Nigeria, Sudan | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Bolivia, Canada, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America | Brazil, Chile, Cuba, El Salvador, Mexico, Nicaragua, Venezuela | 19 | ||
| Asia | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, Nepal, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | Afghanistan, Cambodia, China, India, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Qatar, Yemen | Japan, Lebanon, Myanmar | Indonesia, Malaysia, Oman, Pakistan, Singapore, Sri Lanka | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, United Kingdom | Ukraine | 40 | ||
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 105 | 24 | 6 | 10 | 145 |
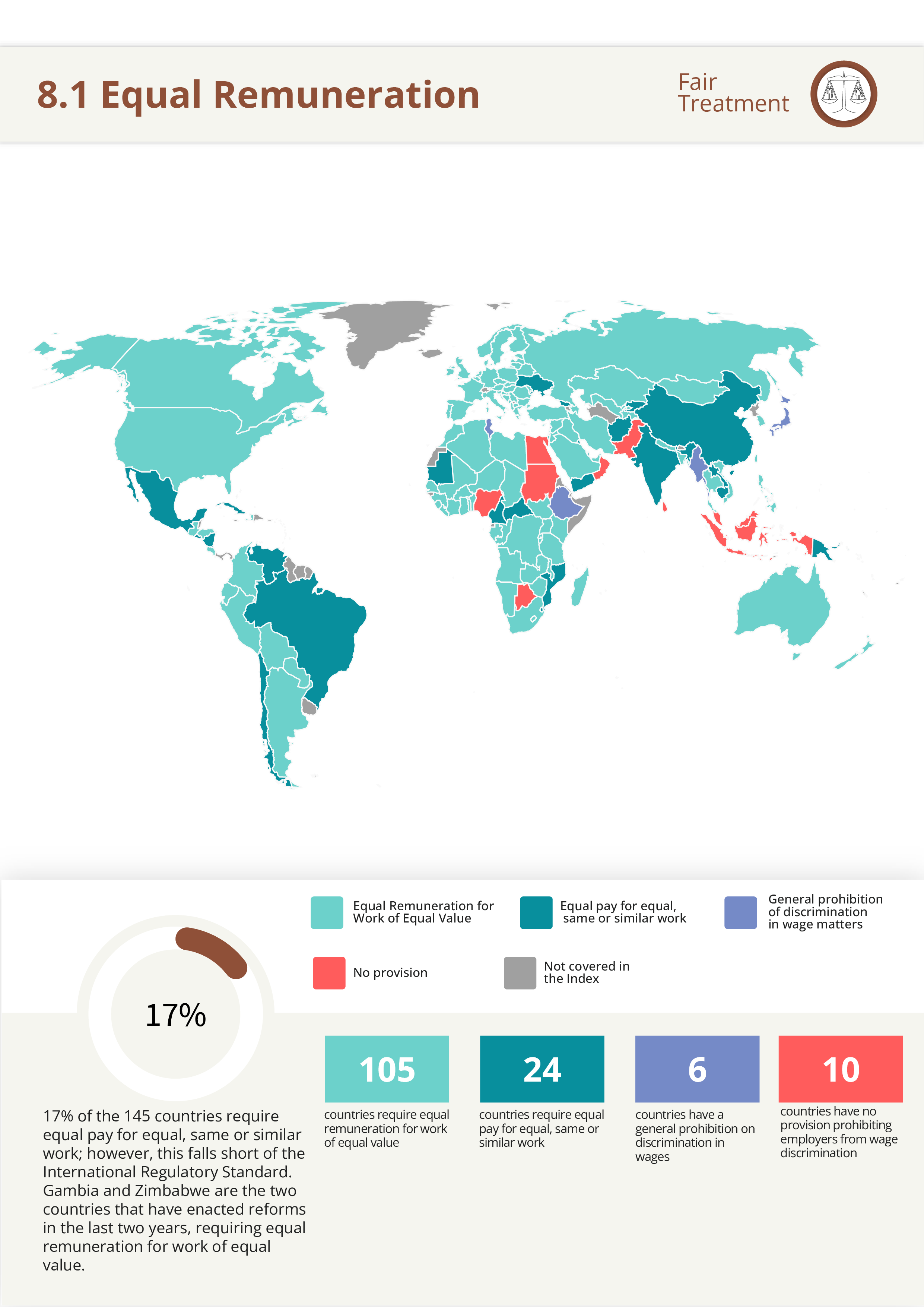
Sexual Harassment in Employment
| Region | Prohibition of Sexual Harassment with criminal penalties | Prohibition of Sexual Harassment with civil remedies | Prohibition of Sexual Harassment with both criminal penalties and civil remedies | General Prohibition | No Prohibition | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Egypt, Gabon, Kenya, Malawi, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Tunisia | Ghana, Namibia, South Africa, Zimbabwe | Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Guinea, Madagascar, Morocco, Mozambique, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | Gambia, Lesotho, Liberia, Libya | Botswana, Eswatini, Mali, Mauritania, Sudan | 45 |
| Americas | Bolivia, Cuba, El Salvador, Haiti, Nicaragua | United Sates of America | Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Honduras, Mexico, Paraguay, Peru, Venezuela | Argentina, Chile | Guatemala | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Bahrain, Cambodia, Iraq, Jordan, Saudi Arabia, Thailand, United Arab Emirates | Azerbaijan, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia | China, India, Indonesia, Israel, Lebanon, Nepal, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Taiwan , Viet Nam | Bangladesh, Japan, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Uzbekistan, Yemen | Iran, Kazakhstan, Myanmar, Syria, Tajikistan | 38 |
| Europe | Bulgaria, Hungary, Moldova, Netherlands | Austria, Czechia, Estonia, Georgia, Germany, Italy, Latvia, Luxembourg, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Serbia, Slovakia, Sweden, United Kingdom | Albania, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, France, Greece, Ireland, Lithuania, Malta, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Romania, Slovenia, Spain, Türkiye, Ukraine | Russian Federation | Belarus | 40 |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | |||
| Total Countries | 32 | 27 | 59 | 14 | 13 | 145 |
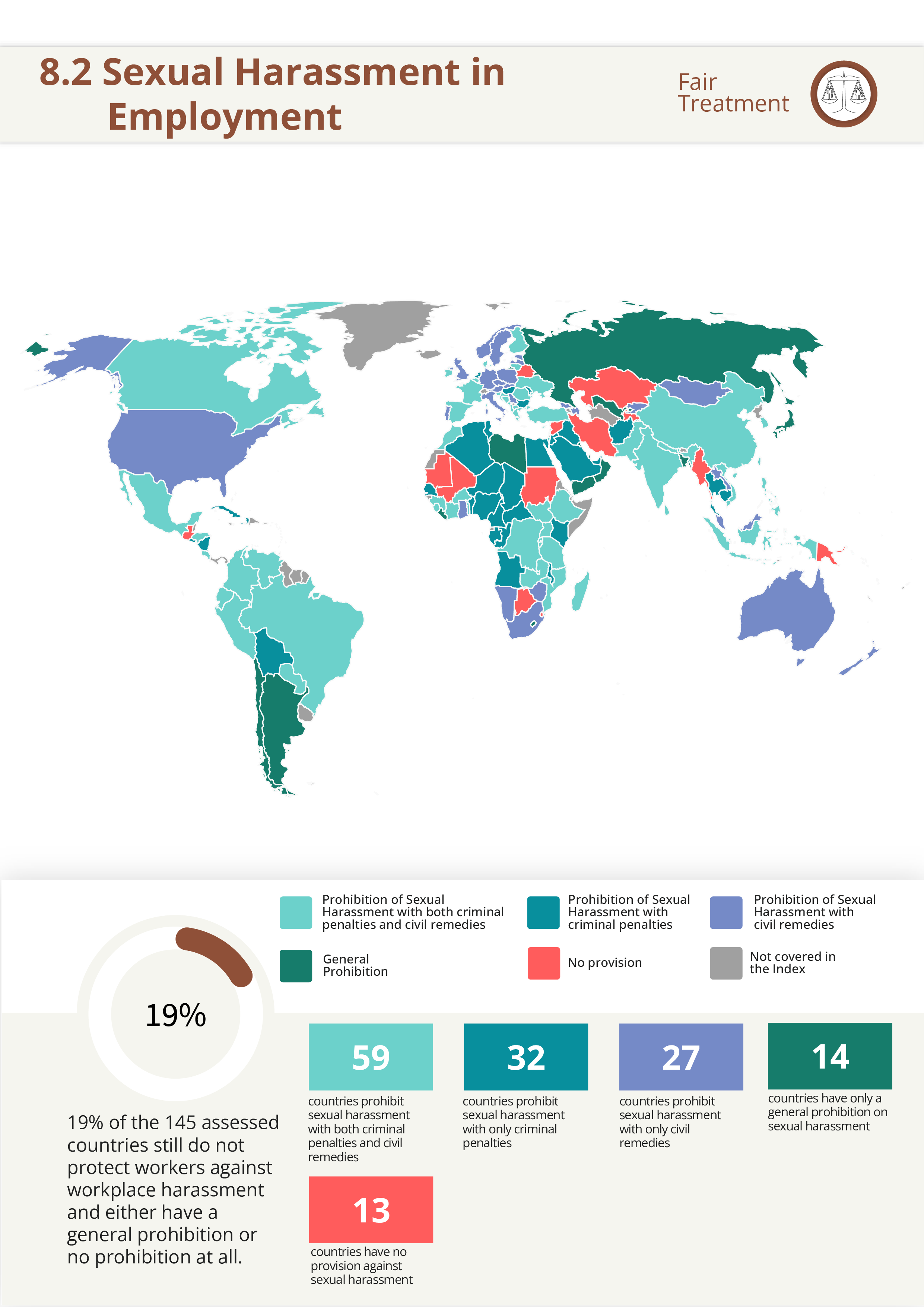
Discrimination in Employment
| Region | Prohibition on Discrimination | No Prohibition | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cabo Verde, Central African Republic, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Algeria, Cameroon, Chad, Congo, Egypt, Gabon, Libya, Mali, Nigeria, Sudan | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | Cuba, Haiti, Guatemala | 19 |
| Asia | Azerbaijan, Cambodia, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Mongolia, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Afghanistan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, China, India, Kuwait, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Thailand | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, Ukraine, United Kingdom | Austria | 40 |
| Oceania | Australia, New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 |
| Total Countries | 110 | 35 | 145 |
Access to same Jobs as Men
| Region | Prohibition to engage in similar jobs | No Restriction | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Algeria, Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Ghana, Guinea, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Morocco, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Sudan, Tunisia | Botswana, Cabo Verde, Côte D'Ivoire, Gabon, Gambia, Kenya, Liberia, Malawi, Namibia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Colombia, Guatemala, Honduras | Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Chile, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Haiti, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Bangladesh, China, India, Iran, Iraq, Israel, Japan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lebanon, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Sri Lanka, Syria, Tajikistan, Thailand, Yemen | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cambodia, Indonesia, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Nepal, Philippines, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Taiwan , United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | 38 |
| Europe | Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Cyprus, Russian Federation, Slovenia, Türkiye, Ukraine | Albania, Austria, Belgium, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden, United Kingdom | 40 |
| Oceania | Papua New Guinea | Australia, New Zealand | 3 |
| Total Countries | 60 | 85 | 145 |
Basic Social Protection for Gig Workers
| Region | Compulsory Coverage | Conditional Coverage | Mixed Coverage | Special Systems | Voluntary Coverage | Universal Coverage (Residents) | Excluded | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Cabo Verde, Côte D'Ivoire, Libya, Mozambique, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia | Algeria, South Africa | Kenya | Egypt, Gabon, South Sudan | Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Gambia, Ghana, Liberia, Malawi, Mali, Namibia, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | Botswana | Benin, Burundi, Chad, Eswatini, Guinea, Lesotho, Madagascar, Mauritania, Morocco, Niger, Nigeria, Senegal, Zimbabwe | 45 |
| Americas | Argentina, Brazil, Ecuador | Canada, Chile, United Sates of America | Cuba | Bolivia, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, Venezuela | Colombia, Guatemala | 19 | ||
| Asia | Azerbaijan, China, Iran, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Oman, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Tajikistan, Thailand | Kyrgyz Republic, Taiwan | Singapore | Mongolia, Nepal | Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, Indonesia, Jordan, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Myanmar, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Syria, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | Israel | Afghanistan, India, Iraq, Lebanon, Pakistan, Yemen | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czechia, Estonia, France, Greece, Hungary, Italy, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Russian Federation, Serbia, Slovenia, Ukraine | Ireland, Portugal, Romania, Sweden, United Kingdom | Latvia, Norway, Slovakia | Belgium, Finland, Germany, Spain | Denmark, Georgia, Poland, Türkiye | 40 | ||
| Oceania | Australia, Papua New Guinea | New Zealand | 3 | |||||
| Total Countries | 46 | 12 | 5 | 10 | 48 | 3 | 21 | 145 |
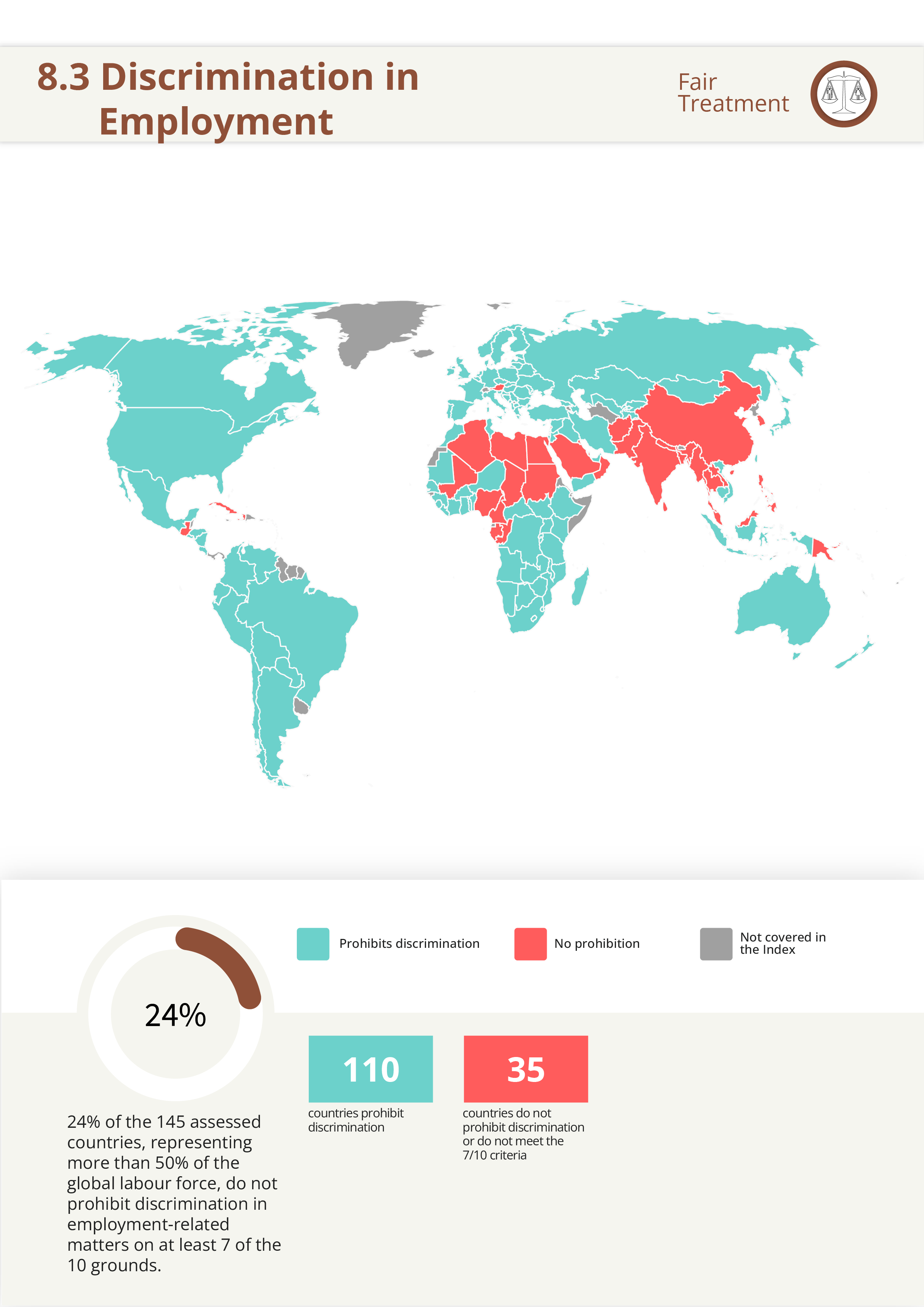
Fair Treatment - country score snapshot