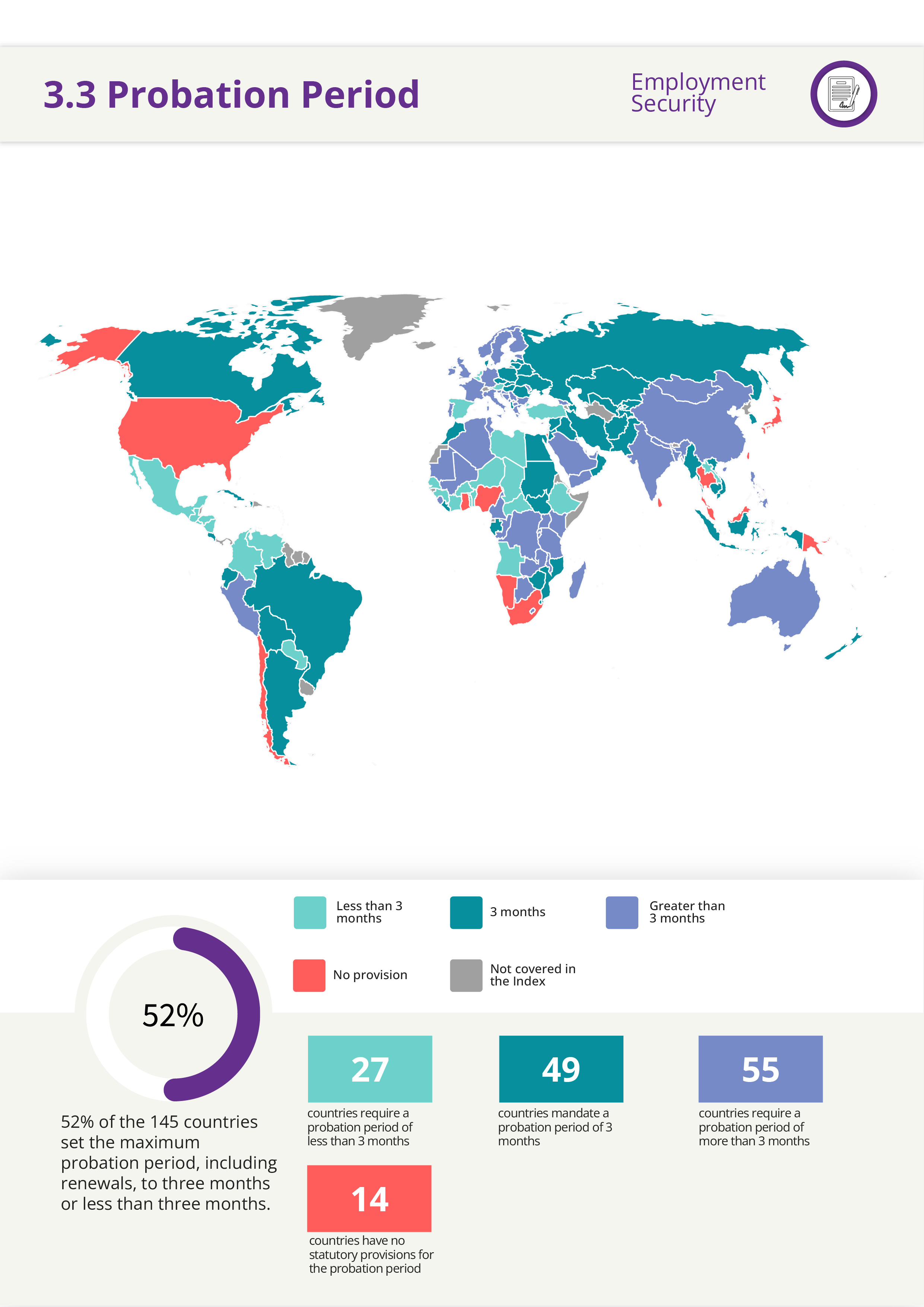
The Employment Security indicator measures whether labour legislation ensures that workers' jobs are characterised by a degree of permanence and reliability.
The indicator considers various aspects of employment security and stability, such as a written employment contract, indefinite vs fixed-term contracts for tasks of a permanent nature, a probation period, a notice period before termination of the contract, and severance pay.
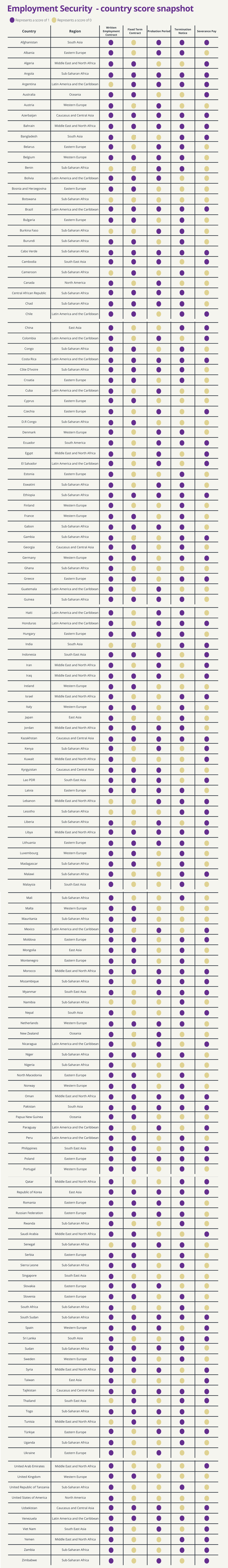
3.1 Written Employment Contract
Does the law require a written employment contract or employment particulars to be given to a worker on commencement of employment?
International Regulatory Standard
- Domestic Workers Convention, 2011 (No. 189)
- Maritime Labour Convention, 2006
- Private Employment Agencies Recommendation, 1997 (No. 188)
Under Articles 7 and 8 of the ILO’s Domestic Workers Convention, 2011 (No. 189), measures are to be taken to ensure that domestic workers are informed of their terms and conditions of employment in an appropriate, verifiable, and easily understandable manner. Preferably, where possible, this should be done through written contracts (enforceable in the country where work is to be done) under national laws, regulations or collective agreements, and with written particulars.
Similar provisions are found in the Standard A2.1 of the ILO’s Maritime Labour Convention, 2006. Moreover, Part II (5) of the Private Employment Agencies Recommendation, 1997 (No. 188) suggests that workers employed by private employment agencies should, where appropriate, have a written employment contract specifying their employment terms and conditions. As a minimum requirement, these workers should be informed of their employment conditions before the effective beginning of their assignment.*
*The two instruments provide necessary guidance on written employment contracts and written particulars: https://www.ilo.org/resource/qas-employment-relationship-and-labour-contracts
Scoring Methodology
Whether employers are required to provide written employment contracts to workers:
1: The labour legislation requires employers to provide written employment contracts or at least written employment particulars to workers on commencement of employment.
0: No legal requirement on the part of employers to provide any such written document (in the form of employment contract or employment particulars).
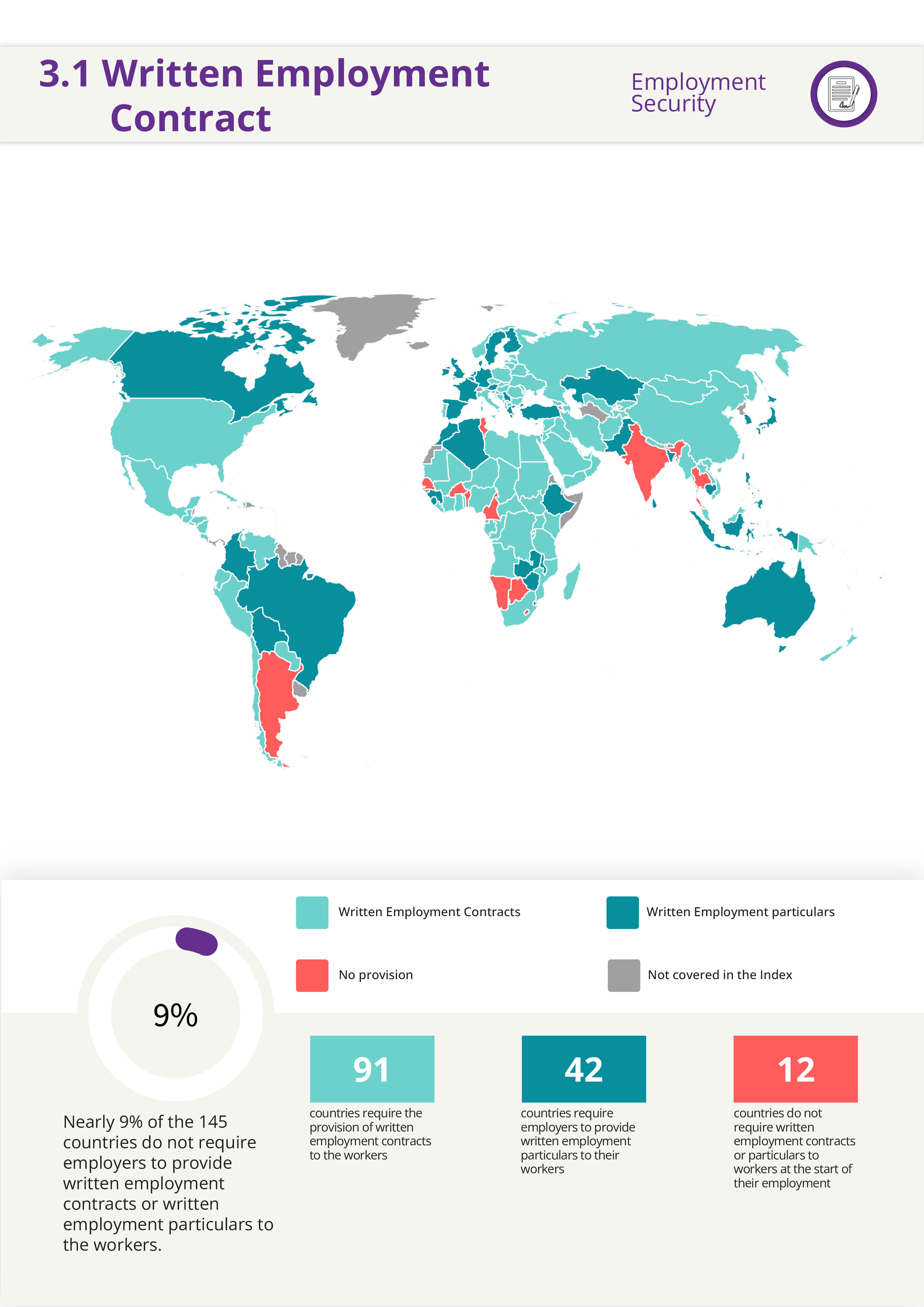
3.2 Fixed Term Contracts
Does the law restrict the hiring of fixed-term contract workers?
International Regulatory Standard
- Termination of Employment Convention, 1982 (No. 158)
- Termination of Employment Recommendation, 1982 (No. 166)
Article 2(3) of the ILO’s Termination of Employment Convention, 1982 (No. 158) states that adequate safeguarding measures should be provided against the use of fixed-term contracts (FTCs) of employment for a specified period of time. This is to ensure that employers cannot avoid the protections stipulated in this Convention.
Also, Paragraph 3(2) of the ILO’s Termination of Employment Recommendation, 1982 (No. 166) allows for a fixed or definite term contract, considering the nature of work or circumstances under which the work is carried out or the interests of the worker. Fixed-term contracts are considered indefinite-term contracts if they are renewed once or more than once, except in the above cases.
Scoring Methodology
Whether labour legislation restricts the hiring of fixed-term contract workers:
1: The maximum length of fixed-term contracts, including renewals, is at most five years.
0: The labour legislation does not specify the maximum length of fixed-term contracts or allow the maximum length of fixed-term contracts, including renewals, to exceed five years.
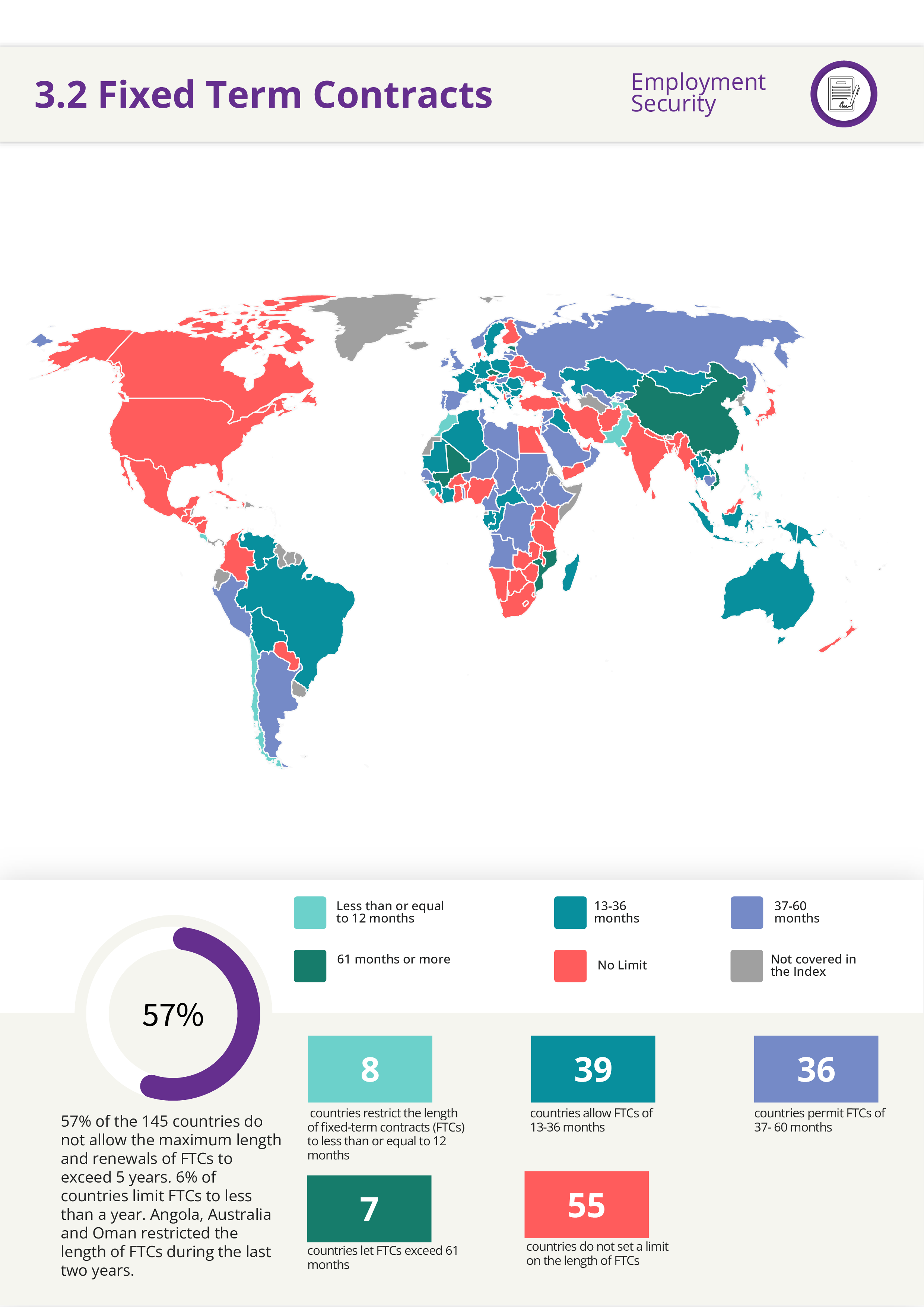
3.3 Probation Period
Does the law limit the length of the probation period, including renewals, to three months?
International Regulatory Standard
- Termination of Employment Convention 1982 (No. 158)
- Termination of Employment Recommendation, 1982 (No. 166)
- Domestic Workers Convention, 2011 (No. 189)
This component is grounded in Article 2(b) of the Termination of Employment Convention 1982 (No. 158). The Convention states that a member may exclude workers serving a period of probation or a qualifying period of employment, determined in advance and of reasonable duration, from all or some of the provisions of this Convention (in essence, the protections afforded under the Convention). The member countries may set a period of probation or a qualifying period of employment, which is determined in advance and of reasonable duration. During this period, the worker does not have access to all employment protections like notice period and severance pay.
Paragraph 1 of the ILO’s Termination of Employment Recommendation, 1982 (No. 166) and Article 7 of the ILO’s Domestic Workers Convention, 2011 (No. 189) also refer to the probation period. In view of this, a probationary period of three months was set as a standard under the Labour Rights Index.
Scoring Methodology
Whether labour legislation limits the length of the probation period to three months:
1: The labour legislation limits the maximum length of the probation period, including renewals, to three months.
0: The labour legislation does not refer to a probation/trial period or allows it to exceed three months.
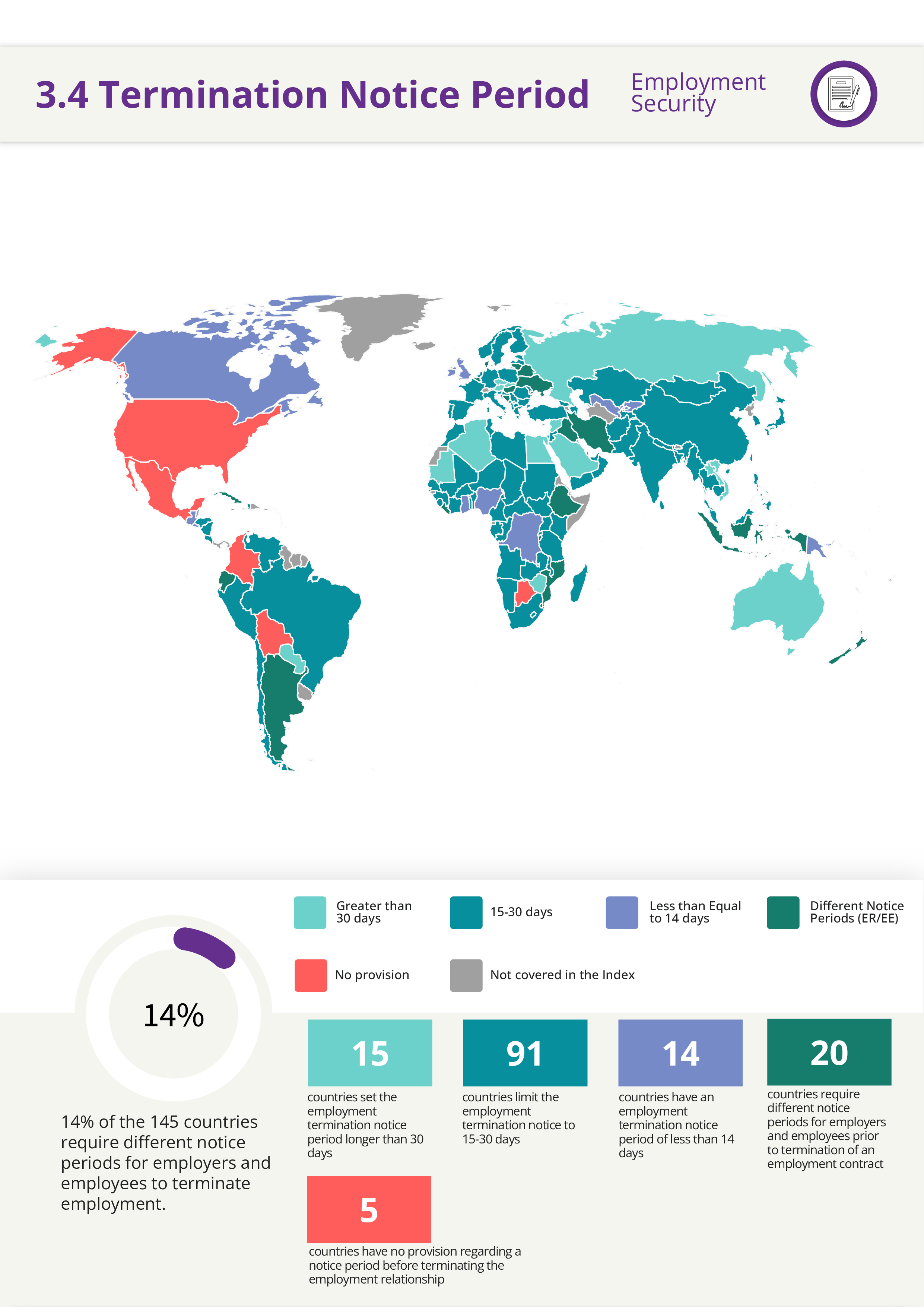
3.4 Termination Notice Period
Does the law require a 30-day notice period before employment contract termination?
International Regulatory Standard
- Termination of Employment Convention 1982 (No. 158)
Article 11 of the ILO’s Termination of Employment Convention, 1982 (No. 158) states that a worker whose employment is to be terminated shall be entitled to a reasonable period of notice or compensation in lieu thereof unless the worker is guilty of serious misconduct - misconduct of such a nature that it would be unreasonable to require the employer to continue the employment during the notice period.*
*For data comparability, a 4-week notice period is also considered equivalent to the 30-day notice period.
Scoring Methodology
Whether there is a 30-day notice requirement before contract termination:
1:
- a) Both the employer and employee can terminate an indefinite term contract after serving a 30-day written notice or paying in lieu of notice, except in cases of gross/serious misconduct; or
- b) where a termination notice required from employees is 30 days, but it is still less than the notice period required of employers; or
- c) where the notice period required from employers is 30 days, but for employees ranges between 14 to 30 days.
0: Both the employer and employee are required to serve a contract termination notice of either less than or more than 30 days.
(*For instance, both parties are required to serve a 14-day written notice or 45-day written notice before termination of employment).
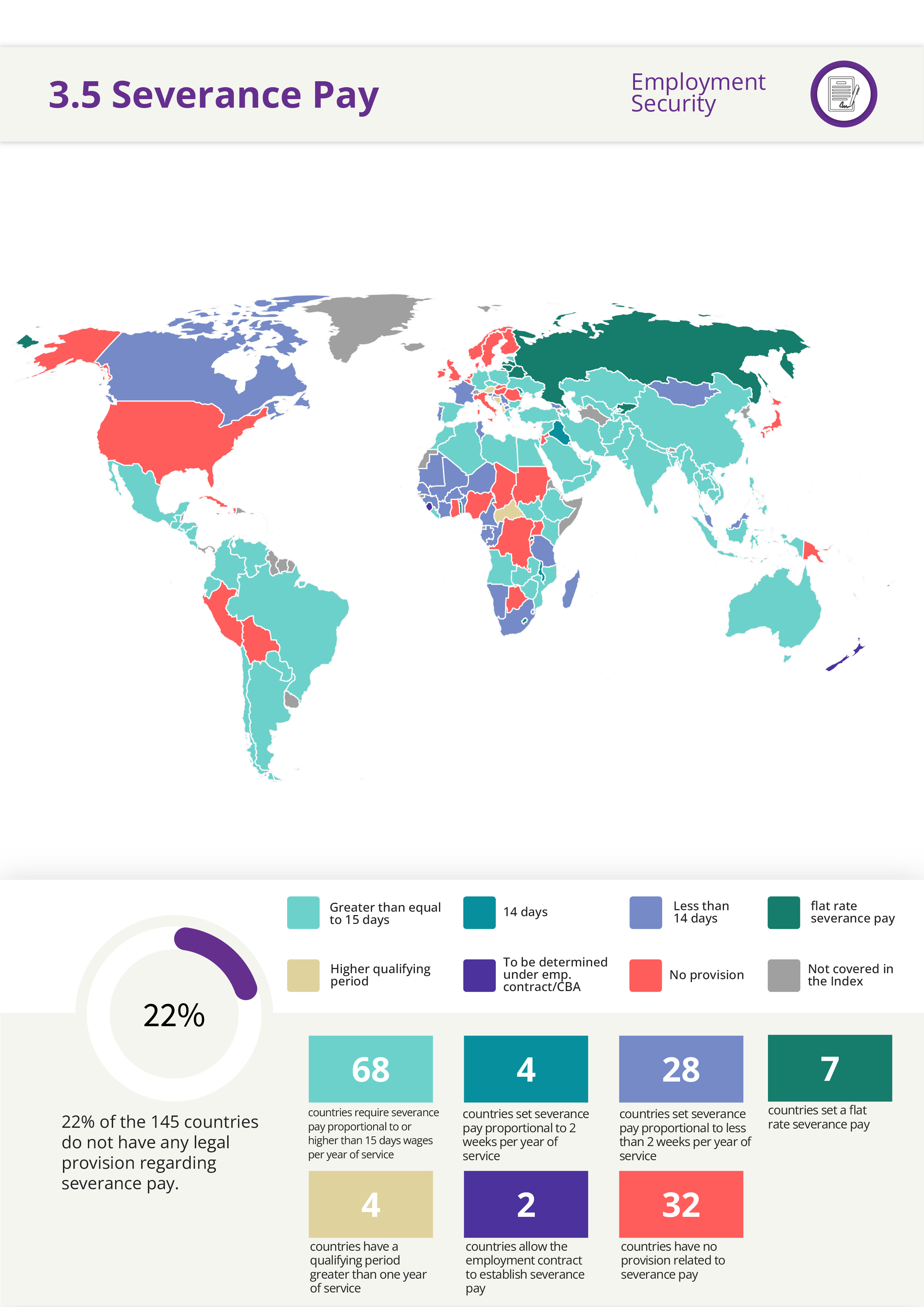
3.5 Severance Pay
Does the law require severance pay at the rate of at least two weeks of wages for every year of service?
International Regulatory Standard
- Termination of Employment Convention 1982 (No. 158)
- Termination of Employment Recommendation, 1982 (No. 166)
Article 12 of the ILO’s Termination of Employment Convention, 1982 (No. 158) states that a worker whose employment has been terminated shall be entitled, in accordance with national law and practice, to a severance allowance or other separation benefits, the amount of which shall be based, among other things, on length of service and the level of wages. It is to be paid directly by the employer or by a fund constituted by employers’ contributions, unemployment insurance benefits or assistance or other forms of social security, or a combination of such allowance and benefits.
Workers who do not fulfil the qualifying conditions for unemployment insurance or assistance or those workers who are terminated for serious misconduct need not be paid any severance allowance or separation benefits solely because they are not receiving an unemployment benefit. Workers whose employment is terminated for serious misconduct are not entitled to any severance allowance or separation benefits. Similar provisions are found in Paragraph 18 of the ILO’s Termination of Employment Recommendation, 1982 (No. 166).
Scoring Methodology
Whether there is severance pay on contract termination:
1: Labour legislation requires employers to provide severance pay (gratuity or end-of-service allowance) at the rate of two weeks’ wages for each year of service* on contract termination in the event of individual dismissal or economic dismissals (redundancy) or on expiry of a fixed-term contract, except in cases of gross misconduct.
0: Severance pay is not required under the law or is provided at a rate lower than two weeks’ wages for each year of service or the rate (for severance pay) is not specified under the law.
*For data comparability, the standard of two weeks’ pay per service year for severance pay was set.
Employment Security - comparative tables
Written Employment Contracts
| Region | Written Employment Contracts | Written Employment Particulars | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Egypt, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Liberia, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania | Algeria, Cabo Verde, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Guinea, Malawi, Morocco, Sierra Leone, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Lesotho, Namibia, Senegal, Tunisia | 45 |
| Americas | Chile, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Peru, United States of America, Venezuela | Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Colombia | Argentina | 19 |
| Asia | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, China, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Kyrgyz Republic, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Bangladesh, Cambodia, Indonesia, Israel, Japan, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Philippines, Republic of Korea, Singapore, Sri Lanka | India, Lebanon, Thailand | 38 |
| Europe | Albania, Belarus, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Estonia, Georgia, Hungary, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Slovenia, Ukraine | Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Malta, Netherlands, Serbia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | New Zealand, Papua New Guinea | Australia | 3 | |
| Total Countries | 91 | 42 | 12 | 145 |
Fixed Term Contracts
| Region | ≤ 12 months | 13-36 months | 37-60 month | ≥ 61 months | No limit | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Burundi, Morocco, Sierra Leone | Algeria, Central African Republic, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Gabon, Guinea, Madagascar, Mauritania | Angola, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ethiopia, Libya, Niger, Senegal, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia | Mali, Mozambique | Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Egypt, Eswatini, Gambia, Ghana, Kenya, Lesotho, Liberia, Malawi, Namibia, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Africa, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia, Zimbabwe | 45 |
| Americas | Chile, Costa Rica | Bolivia, Brazil, Venezuela | Argentina, Peru | Canada, Colombia, Cuba, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Haiti, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, United States of America | 19 | |
| Asia | Pakistan, Philippines, Tajikistan | Indonesia, Iraq, Kazakhstan, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Mongolia, Republic of Korea, Thailand | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cambodia, Jordan, Kyrgyz Republic, Oman, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Uzbekistan | China, Kuwait, Viet Nam | Afghanistan, Bangladesh, India, Iran, Israel, Japan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Myanmar, Nepal, Qatar, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Taiwan , United Arab Emirates, Yemen | 38 |
| Europe | Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Italy, Luxembourg, Montenegro, Netherlands, Poland, Romania, Serbia, Slovakia, Slovenia, Sweden | Hungary, Ireland, Latvia, Lithuania, Malta, Moldova, North Macedonia, Norway, Portugal, Russian Federation, Spain, United Kingdom | Czechia, Estonia | Albania, Austria, Belarus, Denmark, Finland, Türkiye, Ukraine | 40 | |
| Oceania | Australia, Papua New Guinea | New Zealand | 3 | |||
| Total Countries | 8 | 39 | 36 | 7 | 55 | 145 |
Probation Period
| Region | < 3 months | 3 months | > 3 months | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cabo Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Côte D'Ivoire, Ethiopia, Guinea, Libya, Niger, Senegal, Togo | Egypt, Eswatini, Gabon, Liberia, Morocco, Mozambique, South Sudan, Sudan, Zimbabwe | Algeria, Botswana, Burundi, Cameroon, Congo, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gambia, Kenya, Lesotho, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Mauritania, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | Ghana, Namibia, Nigeria, South Africa | 45 |
| Americas | Colombia, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Venezuela | Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Costa Rica, Cuba, Ecuador, Haiti | Peru | Chile, United Sates of America | 19 |
| Asia | Lao People's Democratic Republic | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Cambodia, Indonesia, Iran, Iraq, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyz Republic, Lebanon, Myanmar, Oman, Pakistan, Republic of Korea, Syria, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam | Bangladesh, China, India, Kuwait, Mongolia, Nepal, Philippines, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Yemen | Israel, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, Sri Lanka, Taiwan , Thailand | 38 |
| Europe | Austria, Belgium, Netherlands, Spain, Türkiye | Albania, Belarus, Czechia, Denmark, Hungary, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Romania, Russian Federation, Slovakia, Ukraine | Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, Moldova, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Norway, Portugal, Serbia, Slovenia, Sweden, United Kingdom | 40 | |
| Oceania | New Zealand | Australia | Papua New Guinea | 3 | |
| Total Countries | 27 | 49 | 55 | 14 | 145 |
Termination Notice Period
| Region | ≤ 14 days | 15-30 days | > 30 days | Different Notice Periods | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Nigeria | Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cabo Verde, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Gabon, Gambia, Guinea, Kenya, Lesotho, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Morocco, Namibia, Niger, Rwanda, Senegal, Sierra Leone, South Africa, South Sudan, Sudan, Togo, Tunisia, Uganda, United Republic of Tanzania, Zambia | Algeria, Egypt, Mauritania, Zimbabwe | Burundi, Eswatini, Ethiopia, Liberia, Mozambique | Botswana | 45 |
| Americas | Canada, El Salvador, Guatemala | Brazil, Chile, Costa Rica, Haiti, Honduras, Nicaragua, Peru, Venezuela | Paraguay | Argentina, Cuba, Ecuador | Bolivia, Colombia, Mexico, United Sates of America | 19 |
| Asia | Kyrgyz Republic, Singapore, Uzbekistan | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Israel, Japan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Lebanon, Malaysia, Mongolia, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Sri Lanka, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Yemen | Kuwait, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Viet Nam | Indonesia, Iran, Iraq | 38 | |
| Europe | Cyprus, Ireland, Malta, United Kingdom | Albania, Bulgaria, Croatia, Estonia, Finland, France, Georgia, Germany, Greece, Italy, Latvia, Moldova, Montenegro, Netherlands, North Macedonia, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Spain, Sweden, Türkiye | Austria, Czechia, Russian Federation, Slovakia | Belarus, Belgium, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Denmark, Hungary, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Ukraine | 40 | |
| Oceania | Papua New Guinea | Australia | New Zealand | 3 | ||
| Total Countries | 14 | 91 | 15 | 20 | 5 | 145 |
Severance Pay
| Region | < 14 days | 14 days | ≥ 15 days | Higher qualifying period | Flat rate severance pay | To be determined under emp. Contract/CBA | No Provision | Covered Countries |
| Africa | Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Congo, Côte D'Ivoire, Eswatini, Gabon, Guinea, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Namibia, Niger, Senegal, South Africa, Tunisia, United Republic of Tanzania | Lesotho, Malawi | Algeria, Angola, Cabo Verde, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gambia, Kenya, Liberia, Libya, Morocco, Mozambique, South Sudan, Zambia, Zimbabwe | Central African Republic | Rwanda, Togo | Sierra Leone | Botswana, Burundi, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Nigeria, Sudan, Uganda | 45 |
| Americas | Canada | Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Paraguay, Venezuela | Bolivia, Cuba, Haiti, Peru, United States of America | 19 | ||||
| Asia | Malaysia, Mongolia | Iraq | Afghanistan, Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Bangladesh, Cambodia, China, India, Indonesia, Iran, Israel, Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Lao People's Democratic Republic, Lebanon, Myanmar, Nepal, Oman, Pakistan, Philippines, Qatar, Republic of Korea, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, Syria, Taiwan , Tajikistan, Thailand, United Arab Emirates, Uzbekistan, Viet Nam, Yemen | Albania, Austria, Bosnia and Herzegovina | Kyrgyz Republic | Japan, Jordan, Singapore | 38 | |
| Europe | Croatia, France, Georgia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, Serbia, Slovenia | Moldova | Bulgaria, Czechia, Estonia, Germany, Greece, Poland, Spain, Türkiye, Ukraine | Belarus, Latvia, Lithuania, Russian Federation | Belgium, Cyprus, Denmark, Finland, Hungary, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Romania, Slovakia, Sweden, United Kingdom | 40 | ||
| Oceania | Australia | New Zealand | Papua New Guinea | 3 | ||||
| Total Countries | 28 | 4 | 68 | 4 | 7 | 2 | 32 | 145 |
Employment Security - country score snapshot